How to Choose FR-4 Materials Based on Tg Values for PCB Manufacturing
FR-4 materials are fiberglass-reinforced epoxy laminates commonly used in printed circuit boards (PCBs) due to their strength, electrical insulation, and cost-effectiveness. They are widely used in electronics, telecommunications, automotive, and industrial applications.
However, not all FR-4 materials are created equal. They come with varying glass transition temperatures (Tg), which significantly affect their performance in different operating environments. Choosing the right Tg value for your specific application is crucial, as it ensures that your PCBs can withstand the temperature fluctuations and mechanical stresses they will face during operation. In the following sections, we’ll dive into the importance of selecting the appropriate Tg material for various use cases, helping you make informed decisions that enhance the reliability and longevity of your PCB designs.
What is Tg, and Why Does It Matter in PCB Manufacturing?
Definition of Tg (Glass Transition Temperature)
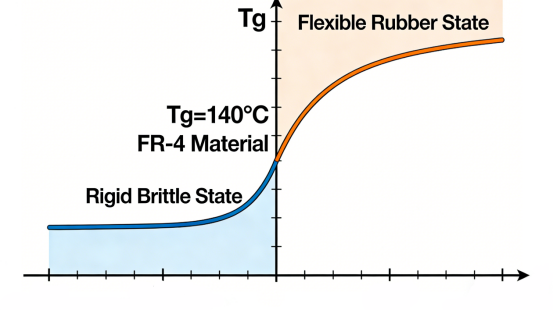
The glass transition temperature (Tg) is the temperature at which a material changes from a rigid, brittle state (like glass) to a more flexible, rubber-like state. For example, FR-4 with a Tg of 140°C remains rigid and maintains its properties below 140°C. Above 140°C, it softens and becomes more flexible.
In PCB manufacturing, understanding the Tg of the materials used (such as FR-4 or other laminates) is essential for ensuring that the board can withstand the operational temperature range without failing.
Tg’s Role in PCB Performance
The Tg value plays a significant role in how PCBs perform in real-world applications. Here’s how:
Electrical Properties: When the temperature of a PCB exceeds its Tg, the material's dielectric properties begin to degrade. This can result in increased signal loss, electrical leakage, and even complete circuit failure. For high-speed circuits, this effect can be particularly damaging, affecting data transmission and causing unreliable performance.
Thermal Properties: A higher Tg allows a PCB to resist thermal expansion and contraction under heat. This is critical for high-power applications where temperature fluctuations are common, such as in automotive systems or telecommunications equipment. Materials with higher Tg values will maintain their shape and performance under heat stress.
Mechanical Properties: Tg also affects the material's mechanical strength. Below the Tg, the material remains hard and rigid, but above it, it becomes more flexible and prone to bending or warping. For PCBs exposed to physical stress—such as in rugged industrial environments or high-vibration applications—materials with a higher Tg can provide better durability.
Consequences of Choosing the Wrong Tg for PCB Design
Choosing the wrong Tg for a PCB can lead to various issues that affect the board’s reliability and performance:
Signal Loss: If the operating temperature exceeds the Tg of the material, the insulating properties of the PCB degrade. For high-frequency circuits, this can lead to signal loss, causing malfunctions or communication failures. This is particularly critical in applications like 5G technology, data centers, and automotive electronics.
Component Failure: Heat is one of the primary causes of component failure in electronic devices. If the material's Tg is too low, the PCB may soften or distort when subjected to heat, potentially leading to the separation of components from the board, solder joint failure, or even total circuit malfunction. This is especially dangerous in safety-critical systems like medical devices or aerospace components.
Thermal Degradation: PCBs exposed to heat cycles or high temperatures can undergo thermal degradation if the material's Tg is too low. This results in warping, delamination, or cracking, which can permanently damage the board. For example, in automotive PCBs, a lower Tg material may not survive the heat generated by engine compartments or other critical areas.
How to Choose FR-4 Materials Based on Tg Values for PCB Manufacturing
When selecting FR-4 materials for PCB manufacturing, the glass transition temperature (Tg) is crucial. FR-4 materials typically have Tg values of 140°C, 155°C, 180°C, and 200°C, each suited for different applications.
Choosing FR-4 with Tg 140°C for Standard Applications
Overview of FR-4 with Tg 140°C: Common Uses and Characteristics
FR-4 with Tg 140°C is one of the most commonly used types of FR-4 materials in PCB manufacturing. It is widely used in consumer electronics and general-purpose applications. The Tg of 140°C indicates that this material can withstand moderate temperature conditions without significant degradation of its properties. This makes it suitable for devices that are not subjected to extreme temperature variations during operation.
Typical characteristics of Tg 140°C FR-4 include good electrical insulation, mechanical strength, and moderate heat resistance. This material is also relatively easy to process and cost-effective, making it ideal for mass production.
Advantages of FR-4 with Tg 140°C
Cost-Effectiveness: FR-4 with Tg 140°C is one of the most affordable options in the PCB market, making it a popular choice for budget-conscious projects.
Ideal for Consumer Electronics: This material offers a balanced performance for everyday devices, such as smartphones, home appliances, and personal gadgets, where high temperature resistance is not a primary concern.
General-Purpose PCB: Tg 140°C FR-4 works well in standard environments, where temperature fluctuations are moderate, and where long-term stability is not a major issue.
Limitations of FR-4 with Tg 140°C
Performance in High-Temperature Environments: FR-4 with a Tg of 140°C cannot perform well in applications exposed to high heat or thermal cycling. The material may soften or lose structural integrity when exposed to sustained temperatures above its Tg.
Reliability Issues: Over time, thermal degradation can occur, especially in applications with prolonged exposure to high temperatures.
Potential for Thermal Expansion: When heated, the material may expand, causing warping or stress on the PCB and components, which can lead to failure in extreme cases.
Best Use Cases for Tg 140°C
Consumer Electronics: Devices such as smartphones, tablets, TVs, and personal computers that operate within moderate temperature ranges.
General-Purpose PCBs: Typical applications include home appliances, office electronics, and other low-to-moderate heat-producing devices that do not require advanced thermal resistance.
Choosing FR-4 with Tg 155°C for Moderate Performance Needs
Overview of FR-4 with Tg 155°C: A Balanced Material for Moderate-Temperature Environments
FR-4 with Tg 155°C offers a middle ground between Tg 140°C and higher Tg materials. It provides better thermal stability, making it suitable for environments with moderate temperature demands. It is often used in applications where higher heat resistance is needed but extreme conditions are not expected.
Advantages of FR-4 with Tg 155°C
Better Thermal Stability: Tg 155°C provides improved heat resistance compared to Tg 140°C, making it more suitable for industrial electronics, automotive systems, and higher-performance consumer electronics.
Balanced Cost-Performance: While it costs slightly more than Tg 140°C, it offers better reliability and thermal performance without a significant price jump.
Moderate Heat Resistance: This material can handle mild thermal fluctuations, making it an ideal option for environments where moderate heat exposure is expected.
Limitations of FR-4 with Tg 155°C
Not Suitable for Very High-Heat Applications: Tg 155°C is still not enough for applications exposed to extreme or fluctuating temperatures (e.g., aerospace or military).
Thermal Cycling Limitations: It may not handle extreme thermal cycling as well as materials with a higher Tg value, limiting its use in applications that require long-term heat stability.
Best Use Cases for Tg 155°C
Industrial Electronics: Equipment used in factories or production lines where moderate heat resistance is necessary.
Automotive PCBs: Used in car electronics that are exposed to moderate heat but are not in the engine compartment or close to high-temperature components.
Consumer Goods: Products that require moderate heat performance, such as coffee machines, microwave ovens, and home entertainment systems.
Choosing FR-4 with Tg 180°C for High-Performance Applications
Overview of FR-4 with Tg 180°C: Performance-Oriented Material Designed for Demanding Applications
FR-4 with Tg 180°C is designed for high-performance PCBs that require superior thermal resistance. This material is suited for applications that experience high temperatures or rapid thermal cycling. The higher Tg value means it can withstand more extreme environments without losing its electrical or mechanical properties.
Advantages of FR-4 with Tg 180°C
Increased Thermal Resistance: With Tg 180°C, the material can handle much higher temperatures, making it suitable for high-power electronics, telecommunications, and automotive electronics.
Better Reliability in Harsh Environments: This material offers superior performance in environments where thermal cycling or mechanical stress are common.
Superior Electrical Performance: Higher Tg values lead to more stable electrical characteristics, especially in high-frequency applications.
Limitations of FR-4 with Tg 180°C
Higher Cost: The FR-4 with Tg 180°C is more expensive than lower Tg materials, which may increase production costs.
Possible Brittleness: The material may become brittle under certain mechanical stresses, which could lead to cracking or breakage in high-vibration environments.
Best Use Cases for Tg 180°C
High-Performance Electronics: Devices such as computers, networking equipment, and telecommunication devices where both heat resistance and high electrical performance are critical.
Automotive PCBs: For automotive electronics that are exposed to higher temperatures or require consistent reliability under extreme conditions.
Devices Subject to Thermal Cycling: Aerospace electronics, medical devices, and industrial equipment that face rapid changes in temperature.
Choosing FR-4 with Tg 200°C for Advanced, High-Durability PCBs
Overview of FR-4 with Tg 200°C: Premium-Grade Material Used in Extreme Conditions
FR-4 with Tg 200°C is a premium-grade material known for its exceptional performance in extreme environments. It is typically used for applications that require maximum durability, high-frequency performance, and superior heat resistance. This material is designed for the most demanding industrial, military, and aerospace applications.
Advantages of FR-4 with Tg 200°C
Exceptional Heat Resistance: With Tg 200°C, this material can handle extreme heat without deforming or degrading, making it ideal for high-power and high-frequency applications.
Superior Mechanical Properties: This material provides excellent dimensional stability and is highly resistant to thermal expansion, which makes it perfect for mission-critical applications.
Ideal for High-Frequency and High-Power PCBs: The Tg 200°C material is particularly suitable for high-frequency circuits, power electronics, and high-reliability systems that operate under harsh conditions.
Limitations of FR-4 with Tg 200°C
Significant Cost Increase: Tg 200°C materials are significantly more expensive than lower Tg options, which may not be justified for standard applications.
Overkill for Standard Consumer Electronics: This material may be too costly and unnecessary for consumer devices like smartphones or home appliances that don’t operate in extreme conditions.
Best Use Cases for Tg 200°C
Aerospace Electronics: Components used in aircraft and spacecraft where temperature extremes and mechanical stress are constant factors.
High-Performance Telecommunications: Used in communication systems, satellites, and high-frequency circuits where stability at extreme temperatures is essential.
Medical Devices: Critical healthcare equipment that requires high-reliability and consistent performance in temperature-sensitive environments.
Comparison of FR-4 Materials Based on Tg Values for PCB Manufacturing
Here's a comparison table for the FR-4 materials based on Tg values to help visualize the differences in their characteristics, advantages, limitations, and best use cases:
| Tg Value | Overview | Advantages | Limitations | Best Use Cases |
| Tg 140°C | Standard material for consumer electronics and general-purpose applications. | - Cost-effective - Ideal for low heat applications - Common in consumer electronics | - Limited heat resistance - Performance suffers in high temperature environments - Potential for thermal expansion | Smartphones, tablets, home appliances, personal computers |
| Tg 155°C | Suitable for moderate-temperature environments with better thermal stability. | - Better heat resistance than Tg 140°C - Balanced cost-performance - Good for industrial electronics | - Not suitable for very high-heat environments - Limited thermal cycling performance | Industrial electronics, automotive PCBs, consumer goods with moderate heat |
| Tg 180°C | Designed for high-performance applications needing more heat resistance and stability. | - Increased thermal resistance - Better reliability under thermal stress - Suitable for high-performance electronics | - Higher cost - Brittleness under mechanical stress | High-performance electronics, telecommunications, automotive electronics, devices with high thermal cycling |
| Tg 200°C | Premium material designed for extreme conditions, offering the highest heat resistance. | - Exceptional heat resistance - Ideal for high-frequency and high-power applications - Superior mechanical properties | - Significantly higher cost - May be overkill for standard applications | Aerospace electronics, military-grade PCBs, high-reliability medical devices, high-performance telecommunications |
Step-by-Step Guide to Choosing FR-4 Based on Tg Values
Choosing the right Tg value for FR-4 is key to ensuring your PCB performs reliably. This guide helps you evaluate environmental conditions, performance needs, and cost to make the best choice for your project.
1. Identify the Operating Environment: Understand Temperature Ranges and Mechanical Stress
The first step is to analyze the environment in which the PCB will operate, considering both the temperature range and mechanical stress that it will endure.
The operating environment plays a crucial role in determining the appropriate Tg value for FR-4 material. PCBs may be exposed to varying temperature conditions depending on their use, such as electronics for home appliances, automotive systems, or aerospace devices.
Temperature Range: If the PCB will be used in an environment with high temperatures, you’ll need a higher Tg to ensure the material maintains its structural integrity and electrical properties. For instance, Tg 180°C is better for devices exposed to high temperatures like automotive electronics.
Mechanical Stress: Consider any potential physical stress such as vibration or bending, which might impact the material. High Tg values generally provide better resistance to mechanical deformation under stress.
For example, a consumer electronic device may only need Tg 140°C since it doesn’t experience extreme temperature fluctuations or heavy mechanical stress, while military or aerospace devices may require Tg 200°C for durability under harsh conditions.
2. Assess the Performance Requirements: Evaluate Signal Integrity, Power Handling, and Component Placement
Evaluate how the PCB's electrical performance, power handling capacity, and component density will affect the choice of Tg value.
The performance requirements of the PCB will guide the decision on the appropriate Tg. These include:
Signal Integrity: Higher Tg values improve the PCB's performance in high-speed applications by reducing signal loss, which is critical for telecommunication equipment or data centers. A Tg of 180°C or higher ensures stable performance in circuits with high-frequency signals.
Power Handling: For devices that handle more power, like high-power LEDs or automotive electronics, the PCB material needs to resist thermal degradation. In this case, a higher Tg material will offer improved heat resistance and power handling capabilities.
Component Placement: Dense PCBs with many components in a small area generate more heat. For high-density PCBs, Tg 180°C or above is often the better choice to prevent thermal issues like delamination and warping.
For example, a smartphone PCB might require Tg 140°C for its low power consumption and component density, while a telecommunications PCB needs Tg 200°C to handle high-frequency signals and power dissipation.
3. Consider Cost Constraints: Decide on the Acceptable Cost for the Desired Performance
Consider the budget constraints and choose the Tg value that provides the necessary performance without exceeding your cost limits.
The cost of FR-4 material increases with a higher Tg, so it’s important to balance performance needs with budget limitations.
Tg 140°C FR-4 materials are the most affordable and ideal for standard consumer electronics where high temperature resistance isn’t crucial.
Tg 200°C materials, while providing superior heat resistance and durability, are more expensive and might be unnecessary for standard applications like consumer electronics.
When choosing the right Tg value, determine how much performance you need and whether you can afford the premium for materials with higher Tg values. For instance, a low-cost TV remote may only need Tg 140°C, while medical equipment requires Tg 180°C or higher for safety and reliability.
4. Choose the Appropriate Tg Value: Based on the Environmental, Performance, and Cost Factors
After evaluating the operating environment, performance requirements, and cost, choose the Tg value that best fits the PCB’s needs.
Once you've gathered information on the environmental conditions, performance requirements, and budget, it’s time to select the appropriate Tg value for your FR-4 material.
For general consumer electronics with moderate heat exposure and low mechanical stress, Tg 140°C may be sufficient.
For industrial electronics or products with moderate power handling needs, Tg 155°C provides a good balance of performance and cost.
For high-performance applications, such as automotive systems or telecommunications equipment, Tg 180°C will offer enhanced thermal and mechanical stability.
For mission-critical systems like aerospace devices, Tg 200°C is essential to ensure the PCB can withstand extreme environments.
A practical example: If designing a home appliance PCB, you may opt for Tg 140°C, while automotive PCBs exposed to high heat would require Tg 180°C.
5. Verify Compliance with Industry Standards: Ensure That the Chosen Material Meets Any Relevant Regulations or Certifications
Ensure that the selected Tg value complies with any industry standards or regulations that apply to your specific application.
Different industries have specific regulations or standards that dictate the minimum required Tg for materials used in PCBs. Ensuring compliance with these standards is critical for safety, performance, and certification.
Automotive, medical, and aerospace industries often require materials with Tg values that exceed standard consumer-grade materials to meet performance and safety certifications.
Check for certifications such as UL certification, RoHS compliance, and IPC standards. For instance, IPC-2221 and IPC-6012 set the standard for PCB manufacturing, including specific guidelines for the Tg of the materials used.
For example, medical devices often require Tg 180°C or higher to comply with safety standards, while consumer electronics may follow more relaxed regulations, allowing for Tg 140°C.
Conclusion
Choosing the right Tg value for FR-4 materials is essential to ensuring your PCB performs reliably in its intended environment. The Tg value directly influences how well the board can handle temperature fluctuations, signal integrity, and mechanical stress. Whether you're designing for consumer electronics, industrial systems, or high-performance applications, selecting the correct Tg based on the operating conditions and performance needs is crucial.
It's important to carefully consider the end-use environment, thermal stability, and mechanical stress your PCB will encounter, as well as your budget. While higher Tg values provide better thermal resistance, they can also come at a higher cost, while lower Tg values are often sufficient for less demanding applications.
At PCBMASTER, we understand that every project has its own unique requirements. As an experienced PCB supplier, we offer a variety of FR-4 materials with different Tg values to match your specific needs. Whether you need Tg 140°C for everyday consumer devices or Tg 200°C for more demanding, high-durability applications, we can help you choose the ideal material for optimal performance and reliability. Let our expertise guide you to the right choice for your PCB project.
FAQs
What does Tg mean in PCB manufacturing?
Tg (Glass Transition Temperature) is the temperature at which the FR-4 material transitions from a rigid, glassy state to a more flexible, rubber-like state. In simpler terms, it marks the point at which the material loses its strength and becomes more susceptible to deformation as it softens.
In PCB manufacturing, Tg is crucial because it affects the thermal stability and mechanical integrity of the PCB. When a PCB operates at temperatures above its Tg, the material may soften, leading to warping, delamination, or failure of solder joints. Therefore, selecting the right Tg ensures that the PCB can handle temperature fluctuations without compromising performance, making it a key factor in PCB design.
Why is Tg 180°C recommended for high-performance PCBs?
Tg 180°C is recommended for high-performance PCBs due to its superior thermal resistance and reliability under extreme conditions. Materials with a Tg of 180°C can withstand higher operating temperatures without experiencing the softening or deformation seen in lower Tg materials.
Thermal Resistance: A Tg of 180°C ensures that the PCB can handle thermal cycling—rapid temperature changes—without losing its integrity. This is particularly important for high-power devices, automotive electronics, or telecommunication equipment, which often experience intense heat due to power dissipation or environmental factors.
Reliability: As Tg 180°C provides better resistance to thermal expansion, it minimizes risks like component misalignment and solder joint failure, which are common in high-performance systems that generate significant heat.
By selecting Tg 180°C, you're ensuring that the PCB will perform reliably in high-temperature environments and maintain signal integrity under stressful conditions, contributing to the longevity of your device.
Can I use FR-4 with a Tg of 140°C in high-temperature environments?
No, FR-4 with a Tg of 140°C is not suitable for high-temperature environments. This material can start to soften once the temperature exceeds 140°C, which significantly reduces its structural integrity and electrical insulation properties.
In high-temperature applications, such as automotive electronics or industrial machinery, the temperature could easily exceed the Tg 140°C threshold, leading to:
Thermal Degradation: The PCB material may begin to deform, causing warping and delamination, which can lead to failure of electrical connections.
Solder Joint Issues: The solder joints used to attach components to the PCB might weaken or break, leading to intermittent connections or complete failure.
Component Failure: Some components may experience overheating or malfunction due to the inability of the PCB to properly dissipate heat.
For these reasons, Tg 140°C is better suited for standard consumer electronics where the temperature rarely exceeds that limit. For higher temperature environments, materials with a higher Tg (e.g., Tg 180°C or Tg 200°C) are recommended.
What happens if I choose the wrong Tg for my PCB?
Choosing the wrong Tg for your PCB can lead to various issues, particularly related to thermal failure, signal loss, and shortened lifespan. Here’s what can happen:
Thermal Failure: If the Tg is too low for the application, the PCB can soften under high temperatures, causing it to warp, delaminate, or suffer from solder joint failures. This can result in device malfunction or complete failure.
Signal Loss: A PCB with a lower Tg might not maintain stable electrical performance in high-frequency circuits. As the material softens, it can lead to signal degradation, affecting the reliability of high-speed electronic devices like telecommunications equipment or computers.
Shortened Lifespan: A PCB with an inappropriate Tg for its operating environment will have a shorter lifespan. Over time, thermal stress can cause irreversible damage to the board, leading to increased failure rates and the need for early replacement.
For example, if a Tg 140°C board is used in an automotive application (which can experience temperatures higher than 140°C), it may fail prematurely, causing costly repairs or replacements.
How does Tg affect the cost of FR-4 materials?
The Tg value of FR-4 materials has a direct impact on the cost. As Tg increases, so does the price of the material, due to the added thermal stability and performance enhancements.
Here’s a quick comparison of the cost differences:
Tg 140°C FR-4: This is the most affordable material and is typically used in consumer electronics and low-power applications. It’s a cost-effective solution but has limitations when it comes to high-temperature environments or thermal cycling.
Tg 155°C FR-4: Slightly more expensive than Tg 140°C, Tg 155°C offers better thermal stability and is used for industrial electronics or products with moderate heat requirements.
Tg 180°C FR-4: The price increases significantly due to its enhanced thermal resistance. This material is suitable for high-performance electronics, automotive, and telecommunications applications.
Tg 200°C FR-4: This is the premium material, offering the highest thermal stability and mechanical strength, but it comes at a higher cost. It’s ideal for aerospace, military-grade PCBs, and other applications that require maximum durability.
In conclusion, higher Tg values provide superior performance but come at a higher cost. When choosing the appropriate Tg, it’s important to balance performance needs with budget constraints to ensure you get the best value for your specific application.
Author Bio
Hi, I'm Carol, the Overseas Marketing Manager at PCBMASTER, where I focus on expanding international markets and researching PCB and PCBA solutions. Since 2020, I've been deeply involved in helping our company collaborate with global clients, addressing their technical and production needs in the PCB and PCBA sectors. Over these years, I've gained extensive experience and developed a deeper understanding of industry trends, challenges, and technological innovations.
Outside of work, I'm passionate about writing and enjoy sharing industry insights, market developments, and practical tips through my blog. I hope my posts can help you better understand the PCB and PCBA industries and maybe even offer some valuable takeaways. Of course, if you have any thoughts or questions, feel free to leave a comment below—I'd love to hear from you and discuss further!