Why Nickel Plating is Essential Before Gold in PCB Manufacturing: Key Benefits
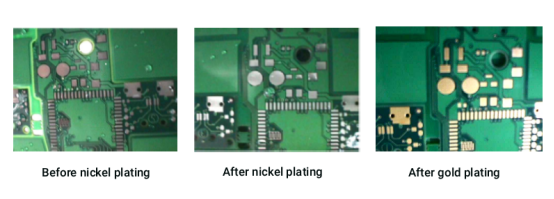
In PCB (Printed Circuit Board) manufacturing, surface plating is a critical process that enhances the board’s performance and durability. Plating involves coating the copper surface with a thin layer of metal, usually gold or nickel, to protect the PCB and ensure reliable electrical connections. Nickel and gold plating are especially important for ensuring long-term functionality and preventing common issues like oxidation or mechanical wear.
Nickel is often applied first because it acts as a barrier between copper and gold. This prevents the two metals from mixing, which could weaken the board and cause failure. The gold layer, then applied on top of the nickel, provides excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance, while also making soldering easier. The combination of these two metals ensures that the PCB can perform reliably in demanding environments, such as high temperatures and high-frequency applications.
By using nickel and gold plating, manufacturers can create PCBs that are more resistant to wear, corrosion, and oxidation, ensuring that the board will continue to function properly over time. This process not only enhances the performance of the PCB but also reduces the risk of failure in critical electronic systems.
What Is the Role of Nickel in PCB Manufacturing?
Nickel helps to prevent the metals from mixing, ensuring the board remains strong, stable, and reliable.
Nickel as a Diffusion Barrier
In PCB manufacturing, nickel plays a crucial role in preventing a problem known as diffusion between copper and gold. Copper and gold are both metals that tend to mix, especially at high temperatures. When gold is plated directly onto copper, the copper atoms can move into the gold layer, while gold atoms can also migrate into the copper. This intermixing forms brittle compounds called intermetallics, which significantly weaken the connection and make it prone to failure.
Nickel prevents this issue by acting as a diffusion barrier. When nickel is plated between the copper and gold layers, it stops the copper and gold from directly interacting. This protective layer ensures that both metals maintain their properties, preventing the formation of these brittle compounds. As a result, the PCB's electrical and mechanical performance remains stable, avoiding weak spots and failures.
The formation of these intermetallic compounds can also cause oxidation. For example, when copper diffuses into the gold layer, it can lead to the formation of copper oxide, which reduces the board’s ability to conduct electricity and makes it difficult to solder. By using nickel as a buffer, these oxidation issues are minimized, helping maintain the board's conductivity and reliability over time.
Nickel’s Contribution to Long-Term Stability
Because nickel has a higher melting point than gold (1455°C for nickel vs. 1064°C for gold), it also helps maintain the purity of the gold layer during high-temperature processes.. In many PCB applications, the boards undergo thermal cycles during soldering or operational use, such as during reflow soldering in electronics assembly. High temperatures can cause gold to degrade if not properly protected. The nickel layer acts as a shield, preventing the gold from diffusing into other layers, which ensures the gold layer retains its integrity. This is especially important for high-performance PCBs used in industries like telecommunications or aerospace, where stability is critical.
By creating a stable interface between copper and gold, nickel helps ensure that the PCB will perform reliably over time, even under harsh conditions. This stability is essential for long-term PCB performance, as it prevents issues like corrosion, oxidation, or weak solder joints that could cause the board to fail prematurely. With nickel acting as a stabilizer, the PCB can continue to function optimally throughout its lifecycle, even in extreme environments or in applications requiring frequent thermal cycling.
How Does Nickel Improve the Mechanical Properties of PCBs?
By providing a smooth surface and a strong, wear-resistant base for the gold layer, nickel ensures that PCBs can withstand physical stress and maintain reliable performance.
Enhancing Surface Flatness with Nickel
Copper surfaces on PCBs are often rough after processes like etching and patterning. This roughness can affect the overall quality of the PCB, especially in high-precision applications. Nickel helps solve this issue by providing a smooth, uniform layer over the copper surface. When nickel is plated onto the copper, it fills in the small imperfections and creates a flatter, more even surface.
A smooth surface is essential for components that require precise placement, such as fine-pitch components or delicate connectors. If the surface is uneven, it can lead to misalignment, poor soldering, and weak electrical connections. By ensuring a flat surface, nickel plating makes it easier to accurately position components, which is especially important in high-density boards and sophisticated electronics.
Providing a Hard, Wear-Resistant Base for Gold
Gold is widely used in PCB manufacturing for its excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance. However, gold is a soft metal and can easily be damaged by wear and tear. This is where nickel plays an important role. Nickel provides a hard, wear-resistant base that supports the gold layer, protecting it from physical damage.
For example, connectors, often referred to as "gold fingers," are exposed to frequent mechanical stress due to repeated plugging and unplugging. Without a hard base, the gold layer could quickly degrade, affecting performance and leading to failure. Nickel, being harder and more durable, significantly extends the lifespan of these connectors by protecting the gold layer from scratches, wear, and micro-vibrations.
What Are the Corrosion-Resistance Benefits of Nickel?
By acting as a barrier between copper and external elements, nickel prevents oxidation and provides an additional layer of defense against environmental factors.
Nickel as a Corrosion Barrier
Copper is highly susceptible to oxidation, a process where it reacts with oxygen in the air, forming copper oxide. This oxide layer can significantly reduce the copper's ability to conduct electricity, leading to performance issues in PCBs. When copper corrodes, it also weakens the mechanical properties of the PCB, potentially causing failures in electrical connections.
Nickel acts as a protective barrier that prevents copper from coming into direct contact with oxygen and moisture in the air. By plating a layer of nickel onto the copper, it effectively shields the copper from oxidation. This barrier preserves the copper’s electrical conductivity and structural integrity, ensuring that the PCB maintains its functionality over time, especially in environments with high humidity or exposure to air.
Double Protection System
The gold layer on a PCB provides excellent corrosion resistance, but it’s not foolproof. While gold itself is highly resistant to corrosion, it can have tiny defects, such as pinholes or micro-cracks. These imperfections can allow moisture and air to reach the copper layer beneath, leading to potential oxidation and damage.
This is where nickel plays a crucial role. The nickel layer acts as an additional line of defense. Even if the gold layer has defects, the nickel underneath provides extra protection to prevent the copper from corroding. This "double protection" system—gold on top and nickel underneath—ensures that the copper remains safe from oxidation, even if the gold layer is compromised. This makes the PCB much more durable and reliable, particularly in harsh environments like electronics exposed to moisture or fluctuating temperatures.
How Does Nickel-Plating Enhance Solderability and Bonding in PCBs?
By providing a stable, smooth surface for soldering and supporting gold wire bonding, nickel improves the durability and consistency of electrical connections.
Improved Soldering Reliability
Nickel plating provides a stable and reliable surface for soldering, which is critical for ensuring strong, durable solder joints on PCBs. Soldering to a nickel layer, as opposed to directly onto copper, offers several advantages. First, nickel’s consistent and smooth surface ensures better adhesion of the solder, which results in a stronger bond. Copper, by contrast, can oxidize easily, which creates an unstable surface for soldering. This oxidation can lead to weak solder joints and poor electrical connections.
Additionally, nickel’s resistance to oxidation means the surface remains clean and free from contamination during the soldering process. As a result, solder joints made on nickel-plated surfaces are more reliable, less prone to failure, and more resistant to environmental factors like heat or moisture. This is especially important in applications where the PCB will undergo repeated thermal cycling, such as in automotive or aerospace electronics.
Key Benefits for Wire Bonding
Nickel also plays a crucial role in wire bonding for chip packaging, particularly with gold wire bonding. In wire bonding, a thin gold wire is used to create electrical connections between the chip and the PCB. For this process to be effective, the bonding surface must be hard enough to support the gold wire and maintain a strong bond.
Nickel provides a hard, durable base that supports the soft gold wire, ensuring a consistent and strong bond. Without nickel, the gold wire might not adhere well or could break under mechanical stress. The hardness of nickel improves bonding strength, ensuring that the connection is stable and reliable over time, even under mechanical stress or vibration.
This feature is critical in high-performance applications like semiconductor packaging, where the strength and consistency of wire bonds directly impact the overall reliability of the electronic device. By offering a solid base for gold wire bonding, nickel helps ensure the long-term performance and durability of the PCB in demanding environments.
How Does Nickel-Plating Help Reduce the Cost of PCB Manufacturing?
By minimizing the amount of gold needed and offering a durable base layer, nickel helps manufacturers achieve cost savings without compromising on quality.
Gold Layer Minimization
Gold is a precious metal, and its cost can significantly increase the price of PCB manufacturing. However, by using nickel plating as a base layer, manufacturers can reduce the thickness of the gold layer needed on the PCB surface. Typically, gold layers on PCBs are very thin, ranging from 0.05 to 0.2 micrometers. The presence of a nickel layer beneath the gold allows for a much thinner gold coating without compromising its functionality. Nickel helps maintain the stability and performance of the PCB, even with less gold.
Using thinner gold layers helps lower material costs while still providing the benefits of gold, such as excellent electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and solderability. This reduction in gold thickness has a direct positive effect on the cost of manufacturing, especially in high-volume production where gold prices can add up quickly.
Cost-Effective Alternative Without Performance Compromise
The combination of nickel and gold creates a cost-effective solution that does not compromise the PCB’s performance. Nickel plating provides mechanical strength and corrosion resistance, while the thin gold layer on top ensures excellent electrical conductivity and solderability. This synergy between nickel and gold ensures the PCB meets industry standards for performance, without requiring the use of excessive amounts of gold.
This balance of performance and cost efficiency is especially important in mass manufacturing, where reducing material costs without affecting quality is a key factor. By using a nickel base and a thin gold finish, manufacturers can keep overall production costs lower, making this method ideal for large-scale PCB production. For example, in consumer electronics, where cost-efficiency is critical, this approach ensures that the product remains affordable while still meeting performance requirements.
Why Is Nickel Plating Essential for High-Performance and High-Reliability PCBs?
Nickel plating provides essential protection against harsh environments, extending the lifespan and stability of the PCB.
Ensuring Consistency and Durability in Harsh Environments
Nickel plating is essential for ensuring the longevity and reliability of PCBs, especially in demanding applications such as aerospace, automotive, and telecommunications. These industries often require PCBs to function in extreme conditions—high temperatures, humidity, and mechanical stress. Without proper protection, PCBs may experience degradation, reduced performance, or even failure.
Nickel plays a crucial role in protecting the PCB from environmental factors. It provides a durable layer that shields the copper base from oxidation and corrosion, both of which can compromise the PCB’s performance. In aerospace, for example, where circuits are exposed to fluctuating temperatures and vibrations, nickel helps maintain the integrity of the electrical connections. Similarly, in automotive electronics, which are subjected to high temperatures and moisture, nickel ensures that the PCB continues to perform reliably over time. This extended durability is vital for the safe and effective operation of critical systems, such as engine control units or communication devices.
Application Scenarios Where Nickel is Crucial
Nickel plating is especially important in specific applications where high-performance and reliability are paramount. One such area is high-frequency circuits, where even minor degradation can lead to signal loss or interference. The combination of nickel and gold plating ensures that these circuits maintain their electrical properties, such as low resistance and minimal signal degradation, even in harsh environments.
Another key area is connectors, particularly those used in high-reliability applications like aerospace and telecommunications. These connectors experience repeated mechanical stress due to frequent plugging and unplugging. Nickel plating provides a hard, wear-resistant base for the gold layer, which ensures the connectors remain durable, corrosion-resistant, and functionally effective over time. This is crucial for maintaining strong electrical connections, preventing signal disruption, and avoiding system failures in critical applications.
Conclusion
Nickel plating plays a vital role in PCB manufacturing by providing multiple benefits that enhance the performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness of the final product. From blocking copper-gold diffusion to improving mechanical strength and offering corrosion resistance, nickel ensures that PCBs function reliably over time, even in challenging environments. It also enhances solderability, supports wire bonding, and reduces the amount of expensive gold needed, making PCBs more affordable without compromising on quality.
In conclusion, nickel plating is not just a critical step in the manufacturing process; it's an essential element for ensuring the longevity, performance, and cost efficiency of PCBs, particularly in advanced applications like aerospace, automotive, and telecommunications. Without nickel, the performance and reliability of modern PCBs would be significantly compromised. For more insights or to explore PCB solutions tailored to your needs, feel free to reach out to PCBMASTER, your expert in high-quality PCB manufacturing.
FAQs
What happens if nickel is not plated before gold on a PCB?
If nickel is not plated before gold on a PCB, several issues can arise. The primary problem is diffusion—when gold is plated directly onto copper, copper atoms can migrate into the gold layer, and gold atoms can diffuse into the copper layer. This interaction forms brittle intermetallic compounds, which can severely weaken the mechanical properties of the PCB, leading to failure in electrical connections or solder joints.
Additionally, oxidation becomes a major concern. Copper is highly prone to oxidation, and when gold is plated directly on copper, the gold layer may not be able to fully protect the copper from oxygen exposure. This can lead to oxidation under the gold layer, increasing electrical resistance and reducing the overall solderability of the PCB. The absence of nickel as a protective layer would significantly decrease the reliability and longevity of the PCB, especially in harsh or high-temperature environments.
Can the thickness of the nickel layer vary?
Yes, the thickness of the nickel layer can vary depending on the specific requirements of the PCB design and the application. Typically, the nickel layer ranges from 2 micrometers (µm) to 5 micrometers (µm) in most applications. Thicker nickel layers can provide better protection against diffusion and corrosion but may increase material costs. Thinner layers may be sufficient for less demanding environments, where cost savings are a priority. The nickel thickness directly influences the overall durability and the ability of the PCB to withstand thermal and mechanical stresses. For high-reliability applications, such as aerospace or military-grade PCBs, a thicker nickel layer is often preferred to ensure maximum protection and stability.
Does the type of nickel plating (electroless vs. electroplating) affect the performance?
Yes, the type of nickel plating—electroless nickel plating versus electroplating—can affect the PCB's performance.
Electroless nickel plating involves a chemical reaction that deposits a uniform nickel layer onto the surface without the need for an external electric current. This method provides a more even coating, especially on complex or irregular surfaces, and ensures that the nickel layer is consistent in thickness across the PCB. It is particularly beneficial for ensuring high-quality corrosion resistance and uniformity.
Electroplating involves the use of an electric current to plate nickel onto the PCB. This method can be faster and less expensive, but the thickness and uniformity of the nickel layer can vary, depending on the plating conditions. Electroplating is often used in situations where the PCB design is simple and uniformity isn't as critical, but it may not be suitable for more complex, high-reliability applications where even plating is necessary.
Both methods provide strong mechanical properties and corrosion resistance, but electroless plating is generally considered superior in ensuring consistency and high performance, especially in demanding applications.
How does nickel-plating affect PCB reliability in extreme temperatures?
Nickel plating significantly improves PCB reliability in extreme temperature conditions. Nickel is highly resistant to thermal cycling and can maintain its structural integrity in both high and low temperatures. In situations where PCBs are exposed to extreme heat, such as in automotive engines or industrial machinery, the nickel layer prevents oxidation and minimizes the risk of thermal damage to the underlying copper.
Nickel’s high melting point (1455°C) and stable nature under temperature fluctuations make it an ideal material for maintaining electrical and mechanical performance in extreme conditions. Without nickel, the gold layer could be more prone to damage or degradation due to the expansion and contraction of materials under high temperatures, potentially leading to failure in critical systems.
Is nickel plating used in all PCBs?
No, nickel plating is not used in all PCBs. While it is common in high-reliability applications (such as aerospace, automotive, telecommunications, and military devices), some simpler PCBs, particularly those used in low-cost consumer electronics, may use alternative plating methods.
For example, OSP (Organic Solderability Preservative) coatings, HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling), or immersion silver or immersion tin are often used in consumer-grade PCBs, where the cost is a more significant concern than the long-term reliability required in high-performance systems. These alternative coatings can offer sufficient protection for lower-cost applications but do not provide the same level of mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, or diffusion protection that nickel-gold plating offers.
Nickel-gold plating is preferred when the PCB will undergo frequent thermal cycling, mechanical stress, or be exposed to corrosive environments. For high-performance systems requiring long-term reliability, nickel is an essential part of the plating process.
Author Bio
Hi, I'm Carol, the Overseas Marketing Manager at PCBMASTER, where I focus on expanding international markets and researching PCB and PCBA solutions. Since 2020, I've been deeply involved in helping our company collaborate with global clients, addressing their technical and production needs in the PCB and PCBA sectors. Over these years, I've gained extensive experience and developed a deeper understanding of industry trends, challenges, and technological innovations.
Outside of work, I'm passionate about writing and enjoy sharing industry insights, market developments, and practical tips through my blog. I hope my posts can help you better understand the PCB and PCBA industries and maybe even offer some valuable takeaways. Of course, if you have any thoughts or questions, feel free to leave a comment below—I'd love to hear from you and discuss further!