PCBA Inspection Guide - A Comprehensive Guide to Circuit Board Component Inspection for Electronics Engineers
In modern electronic products, the quality of PCB Assembly (PCBA) directly determines device performance. Statistics show that 60% of circuit board failures originate from component quality issues. As an electronic engineer with 15 years of experience, I will share the most critical component inspection techniques in PCB assembly to help you build highly reliable electronic products.

1. Resistor Inspection: The "Blood Pressure Monitor" of PCB Assembly
On PCBA production lines, resistor inspection is akin to measuring the "blood pressure" of a circuit board. Three common methods are:
1.1 Wheatstone Bridge Method (Precision Medical-Grade)
• Principle: Accurately measures resistance by balancing a bridge circuit.
• Accuracy: Up to ±0.01%.
• Application: Medical equipment and other precision PCBA inspections.
1.2 Multimeter Rapid Screening Method
• Advantage: Completes single-point detection in 30 seconds.
• Tip: Always power off the circuit before measurement to avoid interference from parallel components.
1.3 Laser Matrix Inspection (Industry 4.0 Solution)
• Efficiency: Inspects 2000+ components per hour.
• Case Study: A automotive electronics factory achieved a 23% improvement in PCBA yield after adoption.
2. Capacitor Inspection: The "Cardiac Function Test" for PCBA
In high-speed PCB assembly lines, capacitor failures are a common cause of system crashes:
▶ Bridge Detection Method
• Accurately measures tiny capacitances down to pF levels.
• Key Note: Eliminate the influence of stray capacitance.
▶ Oscilloscope Dynamic Observation Method
• Advantage: Visualizes charge/discharge curves in real-time.
• Typical Use: Effectiveness testing of power filter capacitors.
3. Diode/Transistor Inspection: The "Nervous System Check" for PCB Assembly
3.1 Dual-Purpose Multimeter Test
• Forward Voltage Drop: 0.3–0.7V indicates normal operation.
• Reverse Resistance: Should exceed 500kΩ.
3.2 Dynamic Characteristic Tester
• Detects nanosecond-level response speeds.
• Essential Equipment: Curve tracer.
3.3 Temperature-Controlled Testing
• Range: -40℃ to 125℃.
• Importance: Mandatory for automotive electronics PCBA.
4. Transistor Inspection: The "Brain Check-Up" for Circuit Boards
[Static Parameter Testing]
• Key Metrics: Beta value (β), saturation voltage drop.
• Industry Standard: IEC 60747 series.
[Dynamic Characteristic Analysis]
• Frequency Response Test: 10Hz–100MHz.
• Case Study: PCB assembly inspection for 5G communication modules.
5. PCBA Inspection Equipment Selection Guide (2024 Update)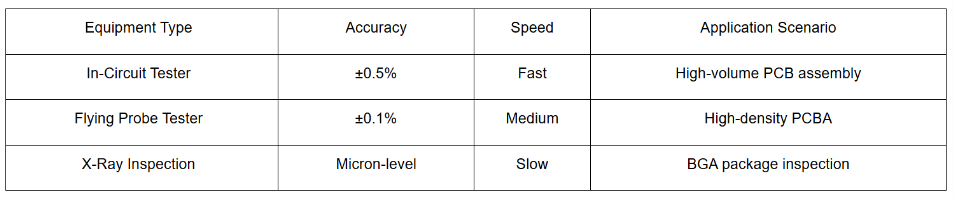
[Engineer’s Advice] During PCB assembly, adopt a "Three-Level Inspection" strategy:
1. Incoming Inspection (Full Check for Critical Components)
2. In-Process Inspection (Sampling at Each Stage)
3. Final Product Inspection (Functional + Environmental Testing)
Through systematic PCBA inspection, a smart home manufacturer reduced product return rates from 5% to 0.3%. Remember: High-quality PCB assembly is not accidental—it is the inevitable result of systematic inspection.
