Top Thermally Conductive Adhesive for PCB Assembly Solutions
Introduction
Using the right thermally conductive adhesive for PCB assembly is vital for managing heat and keeping components firmly attached. This article covers their benefits, types, and selection tips.
Key Takeaways
·Thermally conductive adhesives play a crucial role in PCB assembly by enhancing thermal management and extending the lifespan of electronic devices.
·Different types of thermally conductive adhesives, including epoxies, glues, and thermal pads, provide varying bonding capabilities and thermal performance tailored to specific applications.
·Key factors for selecting a thermally conductive adhesive include thermal conductivity, mechanical and electrical properties, as well as environmental conditions to ensure optimal performance.
Understanding Thermally Conductive Adhesives for PCB Assembly

Thermally conductive adhesives are essential in the realm of PCB assembly, primarily due to their dual role in bonding and thermal management. These adhesives are specifically designed to bond heat-generating electronic components to heat sinks, ensuring that the heat produced is efficiently conducted away from sensitive parts. This not only enhances performance but also extends the lifespan of electronic devices by preventing overheating.
Effective thermal management is indispensable, especially as electronic devices become more compact and powerful. Thermally conductive adhesives work by filling microscopic gaps between surfaces, which improves contact area and reduces thermal impedance. This ensures that the heat is transferred efficiently, maintaining the optimal functioning of the device.
Additionally, these adhesives provide excellent bonding, reducing the need to eliminate mechanical fasteners like clips and screws, which can complicate the assembly process.
Types of Thermally Conductive Adhesives Used in PCB Assembly
Thermally conductive adhesives come in various formulations, each designed to meet specific application requirements. These include thermally conductive epoxy, glue, and thermal pads and films. The choice of adhesive depends on factors such as the type of chemical composition, desired thermal conductivity, and specific application needs.
Thermally Conductive Epoxy
Thermally conductive epoxy adhesives are known for their high thermal conductivity, achieved through the addition of metallic or ceramic fillers. These epoxies, like the 8329TCM, have the following characteristics:
·Often exhibit a smooth, dark grey paste appearance
·Can bond well to a variety of substrates, including metals, ceramics, glass, and most plastics
·Have strong adhesion
·Possess low to moderate viscosity, making them suitable for precise applications.
One of the significant advantages of thermally conductive epoxy is its ability to form thin bonds, which are optimal for heat transfer. Products like the 8329TCS adhesive provide strong adhesion and are highly effective across various materials. Additionally, these epoxies often come in 2-part systems with a 1:1 mix ratio, ensuring ease of use and consistent performance.
Thermally Conductive Glue
Thermally conductive glue, such as the 8329TFF, is a versatile adhesive that sets quickly and bonds strongly to metals, ceramics, glass, and most plastics. Once cured, it becomes thermally conductive and electrically insulating, making it ideal for PCB applications where both heat transfer and electrical insulation are required. The lower viscosity of this glue allows it to be used as a potting compound, adding to its versatility.
Moreover, the 8329TFF adhesive is UL 94 V-0 registered, indicating its flame retardant properties, which enhance its safety and reliability in PCB assembly. This glue simplifies the bonding process compared to mechanical fasteners, ensuring effective heat transfer and structural integrity.
Thermal Pads and Films
Thermal pads and films offer a practical solution for managing heat in PCB assemblies, especially in complex geometries. Their features include:
·Distributing conductive material evenly
·Adjustable thickness to suit specific applications
·Ease of peeling and attaching (particularly thermal pads)
·Availability in electrically conductive or non-conductive types, depending on the application
However, unlike adhesive-based solutions, thermal pads and films may degrade over time, affecting their performance. Despite this, they are still widely used in PCB assembly to redistribute heat from the PCB to the heat sink effectively, ensuring optimal pad functionality.
While they might not conform to surface irregularities as well as thermally conductive adhesives do, metal they provide a viable alternative in many scenarios.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting a Thermally Conductive Adhesive for PCB Assembly
Choosing the right thermally conductive adhesive is critical for ensuring both performance and longevity in electronic applications. Several factors must be considered, including thermal conductivity and resistance, mechanical and electrical properties, and environmental conditions.
Thermal Conductivity and Resistance
The thermal conductivity of an adhesive can be adjusted by altering the level of conductive particles in the filler materials. Poor thermal resistance can lead to system failure, making it essential to evaluate the thermal properties of adhesives carefully. Thermal interface materials help minimize thermal resistance, maintaining efficient heat dissipation and ensuring the device operates within safe temperature ranges. Additionally, thermal expansion must be considered to ensure compatibility with varying temperatures.
Adhesive performance can be significantly influenced by environmental factors. These include humidity, temperature, and chemical exposure over time. Thermally conductive adhesives are designed to withstand harsh conditions, including prolonged exposure to high temperatures and humidity, ensuring reliable performance and longevity.
Surface cleanliness and the appropriate curing method further enhance the durability and effectiveness of these adhesives, ensuring good adhesion.
Mechanical and Electrical Properties
Mechanical and electrical properties are crucial when selecting a thermally conductive adhesive. Correct dielectric strength is necessary for adhesives that serve as electrical insulators, ensuring that electronic components remain protected from electrical interference. Additionally, the mechanical strength of the adhesive must be assessed based on shear, tensile, and compressive forces to ensure it can withstand the stresses of the application.
Surface texture also plays a significant role in adhesion. While rougher surfaces typically improve bond strength, smoother surfaces may require treatment to ensure effective bonding. This consideration is vital for the durability and reliability of the adhesive in various electronic applications, especially in relation to vibration.
Environmental Conditions and Temperature Range
Thermally conductive adhesives must endure varying environmental conditions to maintain their performance. High temperatures, humidity, and repeated thermal cycling can cause adhesives to become brittle over time, affecting their longevity. Therefore, it is essential to choose adhesives that can withstand these conditions without degrading.
Evaluating the specific environmental conditions where the adhesive will be used ensures optimal performance and reduces the risk of adhesive failure. This includes considering the following factors: the operating temperature range, humidity levels, and potential exposure to chemicals.
Application Techniques for Thermally Conductive Adhesives in PCB Assembly
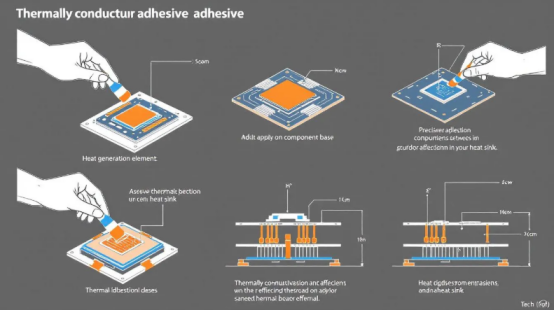
Proper application techniques are essential for ensuring the effectiveness and longevity of thermally conductive adhesives in PCB assembly. This involves surface preparation, dispensing methods, curing processes, and applied techniques.
Surface Preparation
Surface preparation is crucial for achieving strong adhesive bonds and preventing weak bonds that can lead to assembly failure. All substrate surfaces must be clean and free from contaminants to ensure effective bonding. Contaminants such as oils, dust, and residues can significantly diminish adhesive performance, making thorough cleaning a necessary step.
Surface texture also influences bonding strength. Rougher surfaces typically improve adhesion, while smoother surfaces may require treatment to enhance the bond. Properly prepared surfaces ensure that the adhesive can form a strong and durable bond, essential for the longevity of the assembly.
Dispensing Methods
Dispensing methods for thermally conductive adhesives include both manual and automated techniques. Automated dispensing ensures precision and consistency, making it ideal for large-scale production. Manual techniques, on the other hand, offer flexibility for custom or small-batch applications.
The choice of dispensing method depends on the specific requirements of the application and can help determine the intended desired level of precision.
Curing Processes
The curing process significantly impacts the bond strength and performance of thermally conductive adhesives. Curing methods include room temperature curing and heat curing, each with its benefits and considerations. Room temperature curing is convenient and energy-efficient, while heat curing can accelerate the process and enhance bond strength.
Selecting the appropriate curing method is crucial for optimizing adhesive performance and ensuring effective heat transfer in PCB assemblies. The choice of curing method should be based on the specific adhesive used and the requirements of the application.
Common Applications of Thermally Conductive Adhesives in PCB Assembly
Thermally conductive adhesives are widely used in PCB assembly to bond heat-generating components to heat sinks, ensuring efficient heat transfer. They are frequently utilized in power electronics, CPUs, and chip-scale package applications where effective thermal management is critical.
These adhesives are also essential in high-performance equipment like gaming systems and LEDs, where managing heat is crucial for maintaining performance and longevity. Products like LOCTITE’s thermally conductive adhesives enhance the durability and reliability of electronic components by improving heat dissipation.
Advantages of Using Thermally Conductive Adhesives Over Mechanical Fasteners
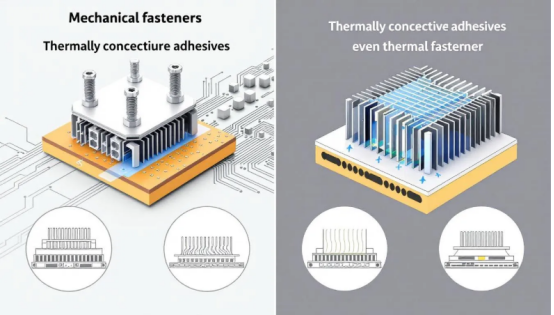
Using thermally conductive adhesives offers several advantages over mechanical fasteners:
·Simplify the assembly process by eliminating the need for screws and clips, reducing complexity and potential points of failure.
·Provide uniform stress distribution, minimizing stress concentration.
·Enhance the overall durability of the assembly.
Additionally, thermally conductive adhesives fill gaps effectively, ensuring better heat transfer and reducing the risk of overheating. This leads to improved thermal management and the longevity of electronic devices.
Popular Thermally Conductive Adhesive Products for PCB Assembly
Several popular thermally conductive adhesive products are available for PCB assembly. Henkel offers a range of adhesives, including:
·liquid
·films
·tapes These are designed for various applications. LOCTITE’s ABLESTIK TE 3530, for example, is specifically formulated for heat-dissipating applications using thermal adhesives.
The 8329TCM thermal adhesive is another notable product, known for its strong adhesion and electrical insulation properties. These products from reputable brands ensure reliable performance and effective thermal management in electronic assemblies.
Summary
In summary, thermally conductive adhesives are indispensable in PCB assembly, providing effective thermal management and strong bonding for heat-generating electronic components. By understanding the different types of adhesives, key selection factors, and proper application techniques, one can ensure optimal performance and longevity of electronic devices. Embracing these advanced adhesives over traditional mechanical fasteners not only simplifies the assembly process but also enhances the overall reliability and efficiency of the devices.
FAQs
Q.What are thermally conductive adhesives used for in PCB assemblies?
A.Thermally conductive adhesives are essential in PCB assemblies for bonding heat-generating components to heat sinks, promoting efficient heat transfer and maintaining structural integrity.
Q.What are the main types of thermally conductive adhesives?
A.The main types of thermally conductive adhesives are thermally conductive epoxy, thermally conductive glue, and thermal pads and films. Each type serves a specific application in enhancing heat transfer in various industries.
Q.Why is surface preparation important when applying thermally conductive adhesives?
A.Surface preparation is crucial for applying thermally conductive adhesives as it removes contaminants and enhances bond strength, ensuring a durable and effective connection.
Q.How do thermally conductive adhesives compare to mechanical fasteners?
A.Thermally conductive adhesives offer advantages such as simplified assembly, uniform stress distribution, and enhanced thermal management compared to mechanical fasteners. Therefore, they may be a more effective solution in applications requiring efficient heat dissipation and structural integrity.
Q.What factors should be considered when selecting a thermally conductive adhesive?
A.When selecting a thermally conductive adhesive, it is crucial to consider thermal conductivity, mechanical and electrical properties, and the specific environmental conditions in which the adhesive will be used. These factors ensure optimal performance and reliability in your application.
Author: Jack Wang
