Printed Circuit Board Standoffs: Essential Components for PCB Stability
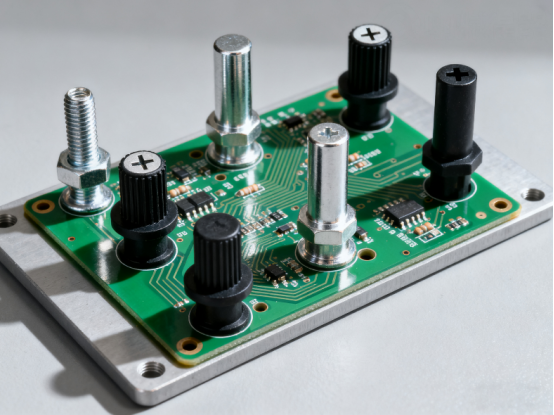
Printed Circuit Board standoffs are small but essential components in electronic devices. They keep the circuit board stable, prevent damage, and ensure everything works safely.
In this article, we will explain why standoffs are important, the different types available, how to choose the right one, and tips for proper installation. By understanding these basics, you can make sure your electronic devices are reliable and long-lasting.
What Are PCB Standoffs?
PCB standoffs are small but critical components used to support printed circuit boards in electronic devices. They keep the board securely fixed inside a case or on a mounting structure, while maintaining a specific distance from other surfaces. This spacing is essential because it prevents the PCB from touching metal parts or other components, which could cause short circuits or mechanical damage.
1. Materials Used for Standoffs
Standoffs are made from different materials depending on the device requirements:
l Plastic – Lightweight and electrically insulating. Plastic standoffs are often used in low-stress environments, such as small consumer electronics, to prevent electrical shorts and reduce weight.
l Metal – Includes copper, aluminum, and stainless steel. Metal standoffs are stronger, more heat-resistant, and suitable for devices that may experience vibration, mechanical stress, or higher temperatures, like industrial machines or automotive electronics.
2. Appearance and Structure
Standoffs typically have a cylindrical shape and can vary in height and diameter depending on the PCB size and clearance requirements.
Some standoffs have internal threads, allowing screws to fasten the PCB firmly. Others are press-fit or snap-in, which makes assembly quicker and easier.
The top and bottom may have flat surfaces or slightly rounded edges to improve stability and prevent component damage.
3. Main Functions of PCB Standoffs
l Mechanical Support – Standoffs keep the PCB rigid, preventing it from bending or flexing, which could damage solder joints or delicate components.
l Electrical Insulation – By lifting the PCB off the mounting surface, standoffs prevent accidental contact with conductive materials, avoiding short circuits and electrical hazards.
l Thermal Management – The space created by standoffs allows airflow under the PCB. This helps dissipate heat from components, keeping the device cooler and extending the lifespan of sensitive electronics.
Ease of Maintenance – Elevated PCBs make it easier to access, inspect, or replace the board during assembly, repair, or upgrades.
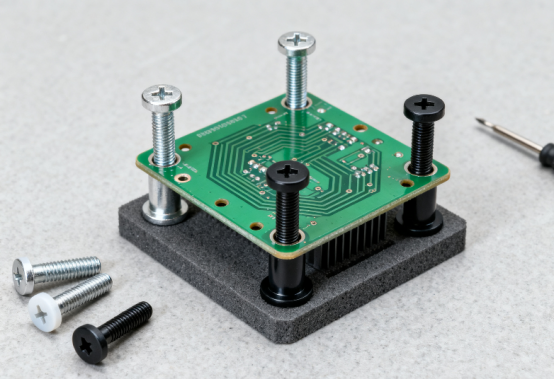
Why PCB Standoffs Are Important
PCB standoffs may seem like small, simple components, but they play a critical role in ensuring that electronic devices work safely and reliably. Without standoffs, a PCB could touch other surfaces, overheat, or sustain damage, which could lead to device failure. Let’s explore in detail why standoffs are essential.
1. Prevent Short Circuits and Mechanical Damage
Standoffs lift the PCB off the mounting surface, creating a safe gap between the board and metal parts. This separation prevents accidental contact that could cause short circuits.
l Short Circuit Prevention – When a PCB touches metal, electricity can flow in unwanted paths, potentially damaging components or causing the device to stop working.
l Mechanical Protection – Standoffs provide a cushion that prevents the PCB from bending or hitting other components during assembly, transport, or use. This reduces the risk of broken solder joints or damaged chips.
For example, in an industrial control panel, standoffs keep the PCB elevated above metal mounting plates, preventing electrical shorts even in a vibration-heavy environment.
2. Enhance Circuit Stability
Electronic devices are often moved, shaken, or subjected to vibration. Standoffs secure the PCB firmly, preventing it from flexing or shifting.
l Vibration Resistance – Devices like automotive electronics or portable medical monitors are exposed to constant movement. Standoffs help the board remain stable under these conditions.
l Prevent Component Damage – By keeping the PCB rigid, standoffs protect delicate components and solder joints from mechanical stress.
In applications like drones or handheld testing devices, stable PCBs reduce the risk of failure and ensure consistent performance.
3. Assist with Thermal Management
Electronic components generate heat during operation. Standoffs create space under the PCB, allowing air to circulate and helping to dissipate heat.
l Improved Airflow – The gap created by standoffs allows cool air to reach the bottom of the PCB.
l Extended Component Life – Lower temperatures prevent overheating, which can damage sensitive components and reduce their lifespan.
l Better Device Reliability – By keeping the PCB cooler, standoffs contribute to the overall stability and longevity of the device.
For instance, in high-performance computing boards or LED driver circuits, proper standoff spacing prevents hotspots and keeps devices running efficiently.
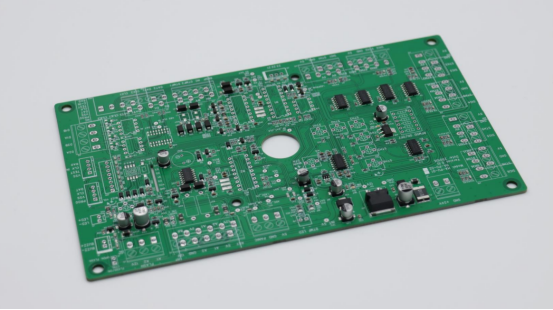
Types and Applications of PCB Standoffs
PCB standoffs come in different types, and choosing the right one depends on the device, environment, and mechanical needs. Understanding the materials, installation methods, and where they are used will help you select the best standoff for your PCB.
1. Classification by Material
l Plastic Standoffs – Lightweight, electrically insulating, and often used in low-stress applications such as consumer electronics or simple circuit boards. They prevent short circuits and are cost-effective. However, plastic standoffs may not handle heavy loads or high temperatures.
l Metal Standoffs – Made from materials like aluminum, copper, or stainless steel, metal standoffs are stronger and heat-resistant, making them ideal for high-stress or high-temperature environments. For example, industrial equipment, automotive electronics, and high-power LED boards often use metal standoffs. However, they can conduct electricity, so careful insulation is required.
2. Classification by Installation Method
l Threaded Standoffs – These have internal or external threads and are fastened with screws. They provide a secure, removable connection, making them ideal for boards that may need maintenance or upgrades.
l Press-Fit Standoffs – These are pushed into holes or slots and stay in place due to friction. They are quick to install but less secure under heavy vibration.
l Pin or Snap-In Standoffs – These can be inserted into PCB holes and lock in place automatically. They are convenient for rapid assembly but may not handle very heavy loads.
3. Applications of Different Types
l Consumer Electronics – Lightweight devices like home appliances or gadgets often use plastic or press-fit standoffs.
l Industrial Equipment – Machines and control panels require metal threaded standoffs to withstand vibration and heat.
l Automotive Electronics – Metal standoffs are preferred for durability and heat resistance in car electronics, sensors, and control modules.
l Medical Electronics – Both plastic and metal standoffs are used depending on the device. For wearable monitors, lightweight plastic standoffs are common, while high-power imaging or diagnostic devices may require metal standoffs for stability and thermal management.
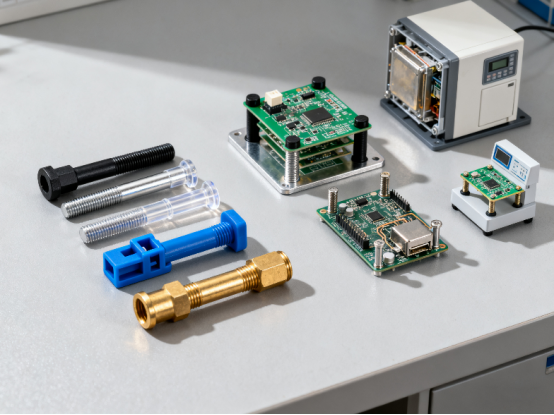

How to Choose the Right PCB Standoffs
Choosing the correct standoffs for your PCB is very important. The wrong standoff can cause the board to become unstable, overheat, or even short circuit. To make the right choice, you need to consider several factors, from the load the board must carry to the environment where it will be used.
1. Key Factors to Consider
l Load Weight – Determine how much weight the standoff needs to support. Heavy components or multiple stacked boards require stronger standoffs, usually metal.
l PCB Thickness – The standoff should match the thickness of the board to ensure stability and proper mounting.
l Installation Space – Consider the space available in the device. The standoff height must provide enough clearance between the PCB and other components or the casing.
l Environmental Temperature – High-temperature environments need heat-resistant materials like metal or specialized high-temperature plastics.
l Insulation Requirements – If the standoff is near live circuits, choose insulating materials like plastic to prevent short circuits.
2. Material Selection Suggestions
l Plastic – Lightweight, cost-effective, electrically insulating. Best for small, low-stress devices.
l Metal – Strong, durable, and heat-resistant. Ideal for industrial, automotive, or high-power applications. Requires careful insulation if near live circuits.
l High-Temperature Materials – Special plastics or ceramics for devices that operate in very hot environments, such as LED drivers or power electronics.
3. Size and Thread Matching
Ensure the standoff diameter fits the PCB hole properly for a tight, stable fit. For threaded standoffs, match the screw size accurately to prevent loosening or stripping. Correct sizing also ensures that the board can be removed easily for maintenance or upgrades without damaging components.
Example: In a medical monitoring device, using the correct threaded standoff size ensures the PCB stays in place even under vibration from daily handling.
4. Common Selection Mistakes and Solutions
l Using weak standoffs for heavy boards – Solution: switch to stronger metal standoffs.
l Choosing too short or too tall standoffs – Solution: measure the required clearance carefully before selection.
l Ignoring insulation needs near live circuits – Solution: select non-conductive materials or add insulating washers.
l Overlooking vibration or heat in the environment – Solution: consider metal or high-temperature standoffs for stability and durability.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can choose the right standoffs to keep your PCB stable, safe, and long-lasting, ensuring your electronic device performs reliably.
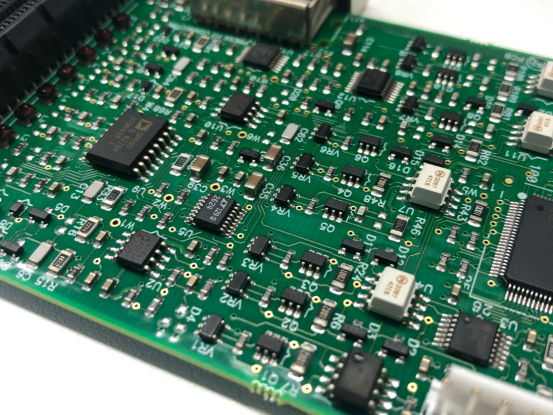
PCB Standoff Installation and Maintenance
Installing PCB standoffs correctly is just as important as choosing the right ones. Proper installation ensures that your PCB remains stable, electrically safe, and durable over time. Regular maintenance also helps prevent failures and extends the lifespan of your device.
1. Installation Steps
l Positioning – First, identify the locations where standoffs are needed. Ensure they align with the PCB mounting holes and provide enough clearance from components and the device case.
l Securing – Attach the standoffs using screws, press-fit, or snap-in methods, depending on the type you selected. Tighten carefully to hold the board firmly without applying too much force.
l Inspection – After installation, check each standoff to make sure the PCB is level, stable, and not touching any metal surfaces. Ensure screws or pins are properly seated and that the board is secure.
2. Key Precautions
Avoiding mistakes during installation is critical for PCB safety and reliability. Over-tightening screws can put too much stress on the board, causing cracks or damage to delicate components. On the other hand, leaving standoffs too loose allows the PCB to move or wobble, which can break solder joints or loosen components over time.
Electrical insulation is another important consideration. Non-conductive standoffs, such as plastic, or the use of insulating washers, can prevent accidental short circuits if the standoff comes near live circuits. Finally, always handle the PCB carefully during installation. Avoid bending, twisting, or scraping the board, as this can damage components and reduce the lifespan of your electronics.
3. Regular Maintenance and Replacement
Routine checks help ensure that standoffs continue to provide stability and safety over the life of the device. In devices exposed to vibration, heat, or frequent handling, inspect standoffs regularly for signs of cracking, wear, or loosening. Even small cracks in plastic standoffs or corrosion on metal standoffs can compromise PCB stability.
If any standoff is damaged or loose, it should be replaced immediately. For high-reliability devices such as medical instruments or industrial electronics, establish a scheduled maintenance routine to verify that all standoffs, screws, and mounting points remain secure. This proactive approach reduces the risk of PCB damage, improves heat management, and ensures that the device continues to operate safely and efficiently.
Conclusion
PCB standoffs may be small components, but they play a critical role in electronic design. They keep circuit boards stable, prevent short circuits, protect components from mechanical damage, and help manage heat. Choosing the right standoffs and installing them correctly ensures that your devices work safely and reliably for a long time.
If you have more questions or want to learn more about PCBs, feel free to contact PCB MASTER. As a professional PCB supplier, they provide high-quality boards and assembly services to help your electronic projects succeed.
FAQs
1. Can PCB standoffs help reduce electronic noise in a circuit?
Yes, PCB standoffs can indirectly help reduce electronic noise. By elevating the PCB above metal surfaces or other boards, standoffs prevent accidental contact that could create unwanted electrical paths. This separation also improves grounding and reduces electromagnetic interference (EMI) in some cases. While standoffs alone do not filter signals, proper placement and insulation contribute to a cleaner and more stable circuit.
2. Are there any special standoffs for high-vibration environments?
Yes. In devices exposed to vibration, like automotive electronics, drones, or industrial machines, standard plastic standoffs may fail. For these applications, metal standoffs or reinforced plastic standoffs are used. Some designs include vibration-damping features, such as rubber washers or flexible mounts, which absorb shocks and prevent the PCB from moving or solder joints from breaking. Choosing standoffs rated for vibration ensures long-term reliability.
3. Can PCB standoffs improve cooling for high-power components?
Absolutely. Standoffs lift the PCB, creating space underneath the board that allows air to flow freely. This airflow removes heat from components such as power regulators, LEDs, or processors. In high-power electronics, adding standoffs can improve natural convection, reduce hot spots, and even allow better placement of fans or heat sinks. Proper standoff selection and placement are key to efficient thermal management.
