Printed Circuit Board Fuses: A Beginner’s Guide to Overcurrent Protection
Figure 1: Printed Circuit Board Fuses
Have you ever seen a circuit board burn out or stop working suddenly? That usually happens when too much electricity flows through it. Too much current can damage the tiny wires on the PCB, burn the components, or even cause sparks and fire. This can ruin your device and cost a lot of money to fix.
This is where a Printed Circuit Board Fuse comes in. A fuse is like a safety guard for your electronics. It stops the electricity when there’s too much, protecting the circuit and the devices connected to it.
Learning about different types of fuses, how they work, and where to use them is very important—especially if you are new to electronics. Once you understand this, you can keep your circuits safe and your devices working longer.
What Are Printed Circuit Board Fuses?
A Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Fuse is a tiny safety device that sits right on the circuit board. Its job is simple: protect the electronic parts on the board from too much electricity.
Here’s how it works: when the electricity flowing through the circuit stays normal, the fuse does nothing—it just lets the current pass. But if too much electricity comes through, the fuse melts or breaks, and this cuts off the electricity. By doing this, it stops the circuit from getting damaged and keeps your device safe.
What makes PCB fuses special?
Small size: They are very tiny, so they fit easily on modern, compact circuit boards.
High integration: Even though they are small, they do a very important job of protecting the whole circuit.
Perfect for modern electronics: From phones to computers, PCB fuses are everywhere because devices are getting smaller and more powerful.
In short, a PCB fuse is like a tiny superhero on your circuit board, always ready to protect your electronics from danger.
Why Do You Need Fuses on a PCB?
Using fuses on a printed circuit board is very important. Let’s go through the main reasons:
1. Prevent Circuit Damage
Without a fuse, too much electricity can flow through the circuit. This can burn out tiny parts like chips, resistors, or wires, and the whole board might stop working. A fuse protects the circuit by breaking the flow before anything gets damaged.
2. Keep People Safe
If a circuit gets too much current, it can spark, overheat, or even start a fire. A fuse cuts the electricity in time, helping to prevent accidents and keep users safe.
3. Lower Repair Costs
If a circuit is damaged without a fuse, you might have to replace the whole board, which is expensive. With a fuse, you only need to replace the tiny fuse, saving money and time.
4. Meet Safety Standards
Electronics must follow industry safety rules, like UL or IEC standards. Using fuses helps devices pass safety tests and ensures they are reliable and safe to use.
In summary, a fuse is like a tiny guardian on your PCB. It protects the circuit, keeps people safe, saves money, and meets safety rules—all at the same time.
Types of Printed Circuit Board Fuses
Every circuit has different needs, and not all fuses work the same way. Before you design or protect a PCB, it’s important to understand the different types of fuses and how each one works.
1. SMD Fuse (Surface-Mount Device Fuse)
SMD fuses are tiny fuses that sit flat on the surface of the circuit board. They are perfect for automatic production because machines can place them quickly and accurately. You often find them in small consumer electronics, like phones, tablets, and other compact gadgets. Even though they are very small, they do an important job of protecting delicate circuits from too much electricity.
2. Through-Hole Fuse (Plug-in Fuse)
Through-hole fuses are larger and go through holes in the PCB. They are commonly used in industrial equipment or devices that handle high power. Their bigger size allows them to handle more electricity safely, making them ideal for circuits where more current flows.
3. PTC Resettable Fuse (Polyfuse)
PTC resettable fuses work differently from regular fuses. When too much current flows, the fuse heats up and limits the electricity. After it cools down, it resets and starts working again. This type is very useful for circuits that need long-term protection without replacing the fuse, saving time and maintenance cost.
4. Fast-Blow vs. Slow-Blow Fuses
Fast-blow fuses react very quickly to overcurrent, which protects sensitive parts like chips. Slow-blow fuses, on the other hand, allow short bursts of high current, such as when a motor starts, but still protect the circuit from long-term overcurrent. Choosing between them depends on the type of device and the behavior of the current in the circuit.
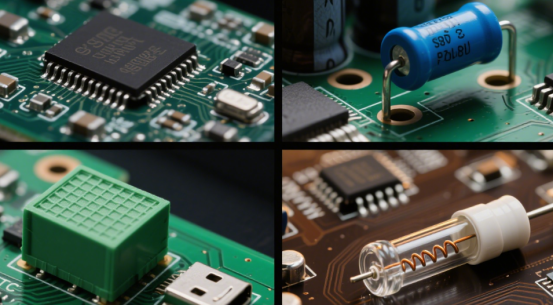
Figure 2: Four Types of Printed Circuit Board Fuses
How to Choose the Right Printed Circuit Board Fuse
Since there are so many types of PCB fuses, you might wonder how to pick the right one for your circuit in real life. Let’s go through the main points to check so you can choose a fuse that truly protects your electronics without causing unnecessary problems.
1. Current and Voltage Rating
The fuse must match the normal electricity your circuit uses. If the rating is too low, the fuse will blow too often. If it is too high, the circuit might get damaged before the fuse reacts. Choosing the correct rating keeps your circuit safe and working properly.
2. Blow Characteristics (Fast-Blow / Slow-Blow)
Some fuses are fast-blow, reacting quickly to any overcurrent to protect sensitive parts. Slow-blow fuses allow short bursts of higher current, such as when a motor starts, but still protect the circuit from long-term overcurrent. Pick the type that suits your circuit and its usage.
3. Physical Size
The size of the fuse depends on the space available on the PCB. Small fuses fit compact boards, while larger fuses are used for high-power circuits. Make sure the fuse fits without interfering with other components.
4. Environmental Conditions
Consider where your circuit will be used. High temperatures, humidity, or vibration can affect the fuse. Choose one that can handle these conditions without failing unnecessarily.
5. Certifications and Standards
Look for fuses that meet safety standards like UL, IEC, or RoHS. These certifications ensure the fuse is reliable, safe, and suitable for commercial or industrial use.
To summarize, choosing the right PCB fuse means checking the electricity rating, blow type, size, environment, and safety standards. Careful selection keeps your circuits safe and devices working well for a long time.
Applications of Printed Circuit Board Fuses
Now that we know how to choose a fuse, let’s look at where PCB fuses are actually used in real life.
1. Consumer Electronics
You can find PCB fuses in everyday devices like smartphones, laptops, and chargers. These fuses protect the tiny circuits inside from sudden spikes in electricity, which could otherwise burn out chips or other components. Without fuses, even a small surge could damage your device and cost a lot to repair.
2. Automotive Electronics
In cars, fuses are used to protect the vehicle’s power system. They keep circuits safe from overcurrent that could happen due to short circuits or electrical faults. This ensures that things like the dashboard, lights, and infotainment system keep working safely.
3. Industrial Control
PCB fuses are also important in industrial machines. In PLCs, motor drivers, and control systems, fuses prevent overcurrent from damaging expensive equipment. By stopping dangerous electricity flow quickly, they reduce downtime and maintenance costs.
4. Medical Devices
Even in sensitive medical equipment, fuses are essential. They protect the delicate electronics inside medical devices from electrical surges, helping to keep both the machines and the patients safe.
Overall, PCB fuses are used everywhere—from the gadgets we use daily to cars, factories, and medical equipment. Wherever there is a circuit that needs protection, a fuse is there to act as a tiny but crucial guardian.
Installation and Design Considerations
When putting a fuse on a PCB, careful planning is very important. Let’s look at the main points to keep in mind.
1. Proper Placement
Place the fuse close to the input power of your circuit. This way, it can quickly stop excessive current before it flows through the rest of the board. A good placement helps protect all the components efficiently.
2. Heat Management
Fuses can get hot when they work, especially during overcurrent. Make sure there is enough space around the fuse and proper airflow so it doesn’t overheat. Overheating can reduce the fuse’s life or even cause it to fail incorrectly.
3. Ease of Replacement or Maintenance
Especially in industrial equipment, it should be easy to remove and replace the fuse when it blows. Designing the layout for quick access saves time and effort during maintenance.
4. Testing and Verification
After installing the fuse, always test the circuit to ensure everything works as expected. Verify that the fuse reacts correctly to overcurrent and doesn’t interfere with normal operation.
So, careful placement, good heat management, easy access, and proper testing will help your fuse protect the circuit reliably and make maintenance simple.
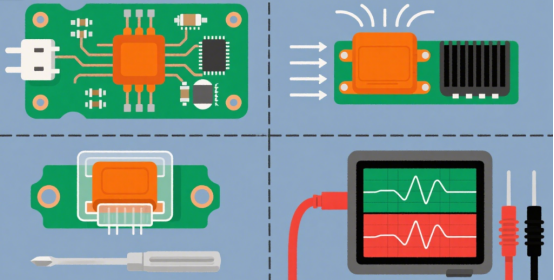
Figure 3: Considerations for Installing and Designing Printed Circuit Board Fuses
Future Trends of Printed Circuit Board Fuses
The world of PCB fuses is always evolving. Let’s look at some important trends that will shape the future.
1. Smaller Packages
Fuses are becoming smaller and more compact to fit on high-density PCBs. Modern devices like smartphones and tablets have very little space on the board, so smaller fuses allow engineers to protect circuits without taking up too much room.
2. Smart Fuses
New types of fuses are being developed that can monitor the current and send feedback. These smart fuses can tell you if a circuit is experiencing too much current before any damage happens. This makes electronics safer and easier to manage, especially in industrial and critical applications.
3. Environmentally Friendly Materials
There is also a focus on eco-friendly and sustainable materials. Fuses that meet RoHS standards help reduce harmful substances and make electronics safer for the environment. This is important for companies that want to produce greener, more responsible products.
In this case, smaller packages, smarter monitoring, and eco-friendly materials are shaping the next generation of PCB fuses, making circuits safer, more efficient, and better for the planet.
Conclusion
PCB fuses are essential safety components in electronics. They protect circuits from too much current and prevent damage to your devices. Without them, even a small electrical surge can cause serious problems.
When designing a circuit, it’s important to choose the right fuse and place it correctly on the board. This ensures your devices stay safe, reliable, and long-lasting.
If you’d like to learn more about PCBs, contact PCB MASTER, a full-service EMS provider offering fast-turnaround PCB solutions for small to medium batches.
FAQs
1. Can a PCB fuse protect my circuit from all types of electrical problems?
No, a PCB fuse mainly protects against too much current. It cannot fix other issues like a short circuit caused by broken wires or software problems.
2. How do I know if a fuse has blown?
Usually, a blown fuse breaks the circuit, so your device stops working. Some fuses are clear or have a small indicator, so you can see if they need replacement.
3. Can I reuse a fuse after it blows?
Most regular fuses cannot be reused once they blow. But PTC resettable fuses can recover after they cool down, so they are useful for circuits that need long-term protection without replacing the fuse.
