Top Printed Circuit Board Fuse Holder Types and Their Applications
In modern electronics, protecting circuits from unexpected surges and overloads is crucial. Even a minor fault can damage sensitive components or interrupt critical operations. One often overlooked but essential component in ensuring safety and reliability is the fuse holder. By securely housing fuses and allowing them to operate effectively, these small devices play a pivotal role across a wide range of applications, from consumer gadgets to industrial systems. Understanding the different types and their uses can make the difference between a robust design and a vulnerable one.
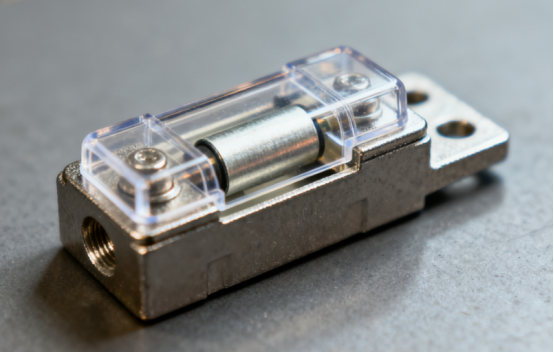
Introduction to Printed Circuit Board Fuse Holders
Definition and Purpose
A printed circuit board (PCB) fuse holder is a small but essential component designed to securely house a fuse on a circuit board. Its primary function is to hold the fuse in place while ensuring a reliable electrical connection between the fuse and the PCB. By doing so, it allows the fuse to operate correctly whenever the circuit experiences excessive current.
The main purpose of a PCB fuse holder is overcurrent protection. In simple terms, if a circuit draws more current than it is designed for, the fuse connected in the holder will “blow” or break the circuit, preventing damage to sensitive electronic components. For example, in a smartphone charging circuit, a fuse holder ensures that a sudden voltage spike doesn’t fry the battery or other internal parts. Compared to directly soldering a fuse onto a board, using a fuse holder makes replacement easier and reduces the risk of soldering damage to the PCB.
Importance in Electronics Design
In modern electronics design, reliability and safety are top priorities. A PCB fuse holder contributes significantly to both. By securely mounting fuses, it ensures that protective devices operate consistently even under vibration, heat, or mechanical stress. This reliability is crucial in applications where circuit failure can have costly or dangerous consequences.
PCB fuse holders are widely used across various industries. In consumer electronics, they safeguard devices like laptops, smart appliances, and gaming consoles. In industrial equipment, fuse holders protect motor controllers, power supplies, and automation systems from overloads. In automotive electronics, they prevent electrical faults in circuits controlling lights, infotainment systems, and battery management systems. In all these cases, the fuse holder acts as a small but critical safeguard, keeping both devices and users safe from electrical hazards.
By combining a secure mounting design with easy fuse replacement, PCB fuse holders provide both practical convenience and essential circuit protection, making them a standard component in robust electronic designs.

Types of Printed Circuit Board Fuse Holders
Through-Hole PCB Fuse Holders
Through-hole PCB fuse holders are designed to be mounted by inserting their leads through holes in the circuit board and soldering them on the opposite side. This mounting technique provides a mechanically robust connection, making them ideal for applications where physical durability is important.
These holders are commonly used in high-current circuits and industrial electronics, such as power supplies, motor controllers, and heavy-duty machinery. Their solid connection ensures that the fuse remains securely in place even under vibration or thermal stress.
Advantages:
Strong mechanical attachment to the PCB.
Can handle higher currents compared to surface-mount designs.
Limitations:
Larger footprint on the PCB, which may be unsuitable for compact designs.
More labor-intensive assembly compared to surface-mount options.
Surface-Mount PCB Fuse Holders
Surface-mount fuse holders are compatible with SMD (Surface-Mount Device) technology and are soldered directly onto the surface of the PCB. Their low-profile design makes them perfect for compact consumer electronics like smartphones, wearables, and small IoT devices.
Advantages:
Saves PCB space and allows for smaller, lighter devices.
Suitable for automated assembly lines, reducing labor costs.
Limitations:
Lower current handling capacity compared to through-hole holders.
Less mechanically robust under high vibration or stress.
Panel-Mount Fuse Holders
Panel-mount fuse holders are designed to be accessible from the exterior of a device, allowing easy replacement of fuses without opening the enclosure. They are widely used in devices that require frequent maintenance or fuse replacement, such as industrial control panels, lab equipment, and consumer appliances.
Advantages:
User-friendly and maintenance-friendly.
Fuse replacement is quick and does not require soldering.
Limitations:
Requires cutouts in the device panel.
Larger physical size may limit compact device designs.
Specialty Fuse Holders
Specialty fuse holders cover a range of unique designs, including miniature holders, high-power holders, and automotive-specific holders. They are often engineered for extreme conditions, offering vibration resistance, high-temperature tolerance, or enhanced durability for critical applications.
Applications:
Automotive electronics, such as battery management systems and infotainment circuits.
Aerospace electronics, where reliability and safety are critical.
Advantages:
Designed for specific operational requirements and harsh environments.
Can handle specialized fuse types and extreme electrical conditions.
Limitations:
Higher cost due to specialized materials and manufacturing processes.
May not be suitable for general-purpose electronics.

Materials and Construction
Common Materials
Printed circuit board fuse holders are made from a combination of insulating plastics and metal contacts, each chosen for durability, safety, and performance.
Plastic Insulation: Most fuse holders use plastics such as ABS, Nylon, or PBT. These materials provide electrical insulation to prevent short circuits and ensure user safety. ABS is cost-effective and moderately heat-resistant, making it suitable for consumer electronics. Nylon offers higher mechanical strength and impact resistance, ideal for industrial applications. PBT provides excellent thermal stability, often used in high-temperature or automotive environments.
Metal Contacts: The conductive parts of a fuse holder are usually made from copper alloys, often coated with nickel or tin plating. Copper ensures good electrical conductivity, while plating protects against corrosion and improves durability. For example, nickel-plated contacts are more resistant to oxidation, which is important in high-humidity or industrial settings. Tin-plated contacts provide cost-effective conductivity with decent corrosion resistance for everyday electronics.
By combining high-quality plastics and reliable metal contacts, manufacturers can create fuse holders that are both safe and long-lasting.
Factors Affecting Durability
The durability of a PCB fuse holder depends on several key factors that engineers must consider during design and selection:
Temperature Ratings: Fuse holders must withstand the operating temperatures of the circuit without deforming or losing insulation properties. High-temperature-rated materials are essential for automotive, industrial, or high-power applications.
Mechanical Strength and Vibration Resistance: In environments subject to vibration or mechanical stress, such as vehicles or industrial machinery, fuse holders must maintain a secure connection and prevent loosening of the fuse. Materials like Nylon and robust mounting designs improve stability under these conditions.
Corrosion Resistance: Metal contacts are vulnerable to corrosion over time, which can reduce conductivity or cause fuse failure. Platings like nickel or tin protect contacts against moisture, chemicals, and oxidation, extending the lifespan of the holder.
Understanding these factors helps designers select fuse holders that will perform reliably under the expected electrical, mechanical, and environmental conditions. For example, a high-current industrial power supply may use a Nylon body with nickel-plated contacts, while a consumer gadget could rely on ABS plastic with tin-plated contacts.

Selecting the Right Fuse Holder
Electrical Specifications
When choosing a PCB fuse holder, the first consideration is the electrical specifications of the circuit. Every fuse holder is designed to support a specific rated current and voltage, which must match or exceed the requirements of the device. Installing a holder with a lower rating can result in overheating or failure, while excessively high ratings may reduce protection effectiveness.
Another critical factor is fuse type compatibility. Fuse holders are designed to work with specific fuse types, such as fast-blow (quick-acting) or slow-blow (time-delay) fuses. Fast-blow fuses are ideal for sensitive electronics that require immediate overcurrent protection, whereas slow-blow fuses can tolerate temporary current spikes without tripping, which is common in motors or inrush-heavy circuits. Selecting the correct fuse type ensures the circuit is protected while avoiding unnecessary interruptions.
Physical and Mechanical Considerations
Physical and mechanical factors also influence fuse holder selection. The PCB footprint and available space determine whether a through-hole or surface-mount holder is appropriate. Through-hole holders are bulkier but mechanically robust, while surface-mount holders save space and support automated assembly.
Accessibility for replacement is another important consideration. Panel-mount or externally accessible holders are ideal for applications where fuses need frequent replacement or maintenance, such as in industrial control panels or laboratory equipment. In contrast, embedded fuse holders are better suited for compact or sealed devices where user access is limited.
Environmental and Safety Factors
Fuse holders must also meet the environmental and safety requirements of the intended application. This includes operating temperature and humidity; for example, automotive or industrial electronics often require holders rated for high heat, vibration, and moisture exposure.
Regulatory compliance is critical to ensure safety and reliability. Look for holders that meet standards such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) or IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission). Compliance guarantees that the fuse holder has passed testing for electrical insulation, flame resistance, and durability under specified conditions.
By carefully considering electrical ratings, mechanical constraints, and environmental factors, engineers can select fuse holders that provide reliable overcurrent protection while fitting the physical and regulatory needs of the application. For example, a compact wearable device may use a surface-mount, low-current holder rated for moderate temperatures, while a high-power industrial supply might require a through-hole holder with high-temperature and UL-certified construction.

Installation and Maintenance
Step-by-Step Installation
Proper installation of a PCB fuse holder ensures reliable overcurrent protection and reduces the risk of circuit failure. The process involves three main steps:
1. Choosing the Correct Fuse:
Select a fuse with the appropriate rated current, voltage, and type (fast-blow or slow-blow) based on the circuit requirements.
For example, a fast-blow fuse is suitable for sensitive electronics, while a slow-blow fuse is better for circuits with temporary current spikes.
2. Mounting the Holder on the PCB:
For through-hole holders, insert the leads into the PCB holes and solder them securely.
For surface-mount holders, align the pads on the PCB and use reflow or hand soldering as appropriate.
Ensure the holder is firmly attached to avoid movement that could cause intermittent connections.
3. Testing Continuity and Proper Operation:
After installation, use a multimeter to verify electrical continuity between the fuse terminals.
Check that the fuse holder provides a stable connection without resistance or short circuits.
This step prevents faulty installation from causing unexpected failures once the device is powered.
Replacement and Troubleshooting
Even with proper installation, fuses may blow over time. Understanding the signs and proper replacement procedure is critical:
1. Signs of a Blown Fuse:
No power in the circuit or device malfunction.
Visible damage to the fuse element, such as a broken wire or darkened glass.
2. Safe Removal and Replacement Procedures:
Disconnect power before handling the fuse holder.
Gently remove the blown fuse, using tweezers or a fuse puller if needed.
Insert a replacement fuse with the same electrical rating and type, ensuring it fits securely in the holder.
3. Common Installation Mistakes to Avoid:
Using a fuse with incorrect current or voltage ratings, which can lead to circuit damage.
Improper soldering or loose mounting, causing poor contact or intermittent operation.
Neglecting environmental factors such as vibration or heat, which can reduce fuse holder lifespan.
Regular inspection and maintenance of fuse holders enhance circuit reliability and prevent unexpected downtime. For example, in industrial control panels, periodically checking fuse holders for secure mounting and corrosion can prevent equipment failures and improve safety.

Comparison of PCB Fuse Holder Types
Through-Hole vs. Surface-Mount
Through-hole fuse holders and surface-mount fuse holders differ in several key aspects:
Footprint and Mechanical Stability: Through-hole holders occupy more PCB space but provide a strong mechanical connection, making them suitable for high-current or high-vibration applications. Surface-mount holders are low-profile and space-saving, ideal for compact electronics.
Current Ratings: Through-hole holders generally support higher currents than surface-mount types, which may be limited by their smaller contacts.
Ease of Assembly and Repair: Surface-mount holders support automated assembly, reducing labor costs, but are harder to replace manually. Through-hole holders are easier to repair or replace, especially in industrial or maintenance-heavy environments.
Example: A motor controller may use through-hole holders for high-current stability, while a wearable fitness tracker uses surface-mount holders to save PCB space.
Panel-Mount vs. Embedded
Panel-mount fuse holders are designed for accessibility, while embedded holders are fully integrated into the PCB:
Accessibility vs. Space Efficiency: Panel-mount holders allow users to replace fuses without opening the device, making them maintenance-friendly. Embedded holders save space and protect fuses from tampering, which is useful in compact or sealed designs.
Application-Specific Pros and Cons: Panel-mount holders are ideal for industrial equipment, lab instruments, or appliances where quick fuse replacement is needed. Embedded holders are suited for compact consumer electronics or devices exposed to harsh conditions, where tamper resistance and protection are priorities.
Example: Industrial power supplies often use panel-mount holders for easy maintenance, whereas laptops or smartphones use embedded holders for space efficiency.
Cost Considerations
The price of fuse holders varies depending on type, materials, and features:
Price Ranges: Surface-mount holders are typically less expensive for mass-produced consumer devices, while specialty or panel-mount holders with high durability can cost more.
Trade-Offs Between Performance and Cost: Choosing a lower-cost holder may save money but could compromise mechanical stability, heat resistance, or accessibility. Investing in a more expensive, high-quality holder ensures long-term reliability, particularly in industrial, automotive, or high-current applications.
Example: A standard surface-mount holder for a low-power IoT device might cost a few cents, whereas a UL-certified panel-mount holder for industrial use could cost several dollars per unit, reflecting the added durability and compliance.

Applications Across Industries
Consumer Electronics
PCB fuse holders are widely used in consumer electronics to protect delicate circuits from overcurrent or short circuits. Common examples include smartphones, laptops, and household appliances. In these devices, fuse holders safeguard batteries, processors, and other sensitive components, preventing damage from power surges or accidental faults. Surface-mount fuse holders are often preferred in compact devices due to their small size and compatibility with automated assembly.
Industrial and Manufacturing Equipment
In industrial and manufacturing environments, fuse holders protect high-power and mission-critical systems. Examples include motor controllers, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), and industrial sensors. Through-hole and panel-mount holders are commonly used in these applications because they offer robust mechanical stability and allow easy replacement during routine maintenance. Ensuring proper overcurrent protection in industrial settings helps prevent equipment downtime and costly repairs.
Automotive and Transportation
Automotive electronics rely heavily on PCB fuse holders for system safety and reliability. Applications include car infotainment systems, engine control units, and battery management systems. Automotive fuse holders are designed to withstand vibration, temperature fluctuations, and harsh environmental conditions. Specialty or high-reliability holders are often used in battery packs or safety-critical circuits to maintain consistent performance over the vehicle’s lifetime.
Aerospace and Defense
In aerospace and defense applications, fuse holders must meet extreme standards for reliability, vibration resistance, and temperature tolerance. These high-reliability holders are used in avionics, and satellite systems. Selection often prioritizes durability and compliance with aerospace regulations, ensuring circuits remain protected even in demanding operational conditions.
Across these industries, PCB fuse holders serve as small but critical components that ensure circuit protection, enhance device reliability, and prevent costly failures. Choosing the right type and material for the specific application is essential to meet both operational and safety requirements.

Future Trends and Innovations
Miniaturization
One of the key trends in PCB fuse holders is miniaturization, driven by the demand for compact and lightweight electronic devices. Modern consumer electronics, wearables, and IoT devices require smaller footprints to save PCB space without compromising functionality. Miniaturized fuse holders maintain electrical performance while enabling slimmer, more efficient designs. For example, a smartwatch may use a tiny surface-mount fuse holder that protects the battery and sensors without increasing the device’s overall size.
Smart Fuse Holders
Another innovation is the development of smart fuse holders, which integrate monitoring or diagnostic capabilities. These holders can detect overcurrent events, track fuse health, or communicate status to a control system. Smart fuse holders are particularly valuable in industrial automation, electric vehicles, and aerospace applications, where predictive maintenance can prevent downtime and costly equipment damage. By providing real-time data, they enhance circuit reliability and operational safety.
Eco-Friendly Materials
Sustainability is becoming increasingly important in electronics design, and PCB fuse holders are no exception. Manufacturers are exploring eco-friendly plastics and recyclable metals to reduce environmental impact. For instance, using PBT or Nylon blends with recyclable additives can lower plastic waste, while tin or nickel plating on copper contacts ensures that materials can be recovered at the end of the product lifecycle. Eco-friendly fuse holders allow designers to meet environmental regulations and support greener electronics manufacturing.
As technology evolves, these trends—miniaturization, smart functionality, and sustainable materials—are reshaping how PCB fuse holders are designed and applied. They offer engineers new opportunities to enhance performance, safety, and environmental responsibility in modern electronic systems.

Conclusion
Printed circuit board (PCB) fuse holders are essential components that protect electronic circuits from overcurrent and prevent damage. They come in various types—through-hole, surface-mount, panel-mount, and specialty holders—each suited for different applications, from compact consumer devices to industrial, automotive, and aerospace systems.
When selecting a fuse holder, it is important to consider electrical specifications, mechanical and physical constraints, and environmental or regulatory requirements. Proper choice ensures reliable operation, safety, and ease of maintenance. Miniaturization, smart monitoring, and eco-friendly materials are shaping the future of fuse holders, offering engineers new ways to optimize performance and sustainability.
For more guidance or specific questions about PCBs, PCBMASTER is ready to provide expert advice and professional solutions for your electronic design and manufacturing needs. Choosing the right fuse holder is a small step that makes a big difference in circuit protection and device reliability.
FAQs
What is the difference between a fast-blow and slow-blow fuse holder?
A fast-blow fuse holder is designed for fuses that react quickly to overcurrent, protecting sensitive electronics from even short, sudden surges. In contrast, a slow-blow fuse holder accommodates fuses that tolerate temporary current spikes without tripping, making them suitable for circuits with motors or inrush currents. The choice depends on whether the circuit needs immediate protection or can handle short-term surges.
Can surface-mount fuse holders handle high-current applications?
Surface-mount fuse holders generally have lower current ratings compared to through-hole types due to their smaller contacts and low-profile design. While they are ideal for compact consumer electronics and automated assembly, they are not recommended for high-current or high-vibration applications, where through-hole or specialty holders provide better stability and current-handling capability.
How do I know which fuse holder type is best for my PCB design?
Selecting the right fuse holder depends on three main factors:
Electrical specifications: Ensure the holder matches the rated current, voltage, and fuse type (fast-blow or slow-blow).
Physical and mechanical constraints: Consider the PCB footprint, mounting style, and accessibility for replacement. Through-hole holders offer strength; surface-mount holders save space.
Environmental and safety requirements: Evaluate temperature, vibration, humidity, and compliance with standards such as UL or IEC. Matching these factors to your design ensures reliable and safe operation.
Are panel-mount fuse holders suitable for automated assembly?
Panel-mount fuse holders are primarily designed for user accessibility, allowing easy fuse replacement from outside the device. They are generally not ideal for automated PCB assembly, as they require cutouts and manual installation. Surface-mount or embedded holders are more compatible with automated production lines.
What are the most common mistakes when installing PCB fuse holders?
Common mistakes include:
Using a fuse with incorrect current or voltage ratings, which can damage the circuit.
Improper soldering or loose mounting, leading to poor electrical contact or intermittent operation.
Ignoring environmental factors, such as vibration or heat, which can reduce the fuse holder’s lifespan.
Failing to test continuity after installation, potentially leaving the circuit unprotected.
