From Resistors to ICs: Key Printed Circuit Board Components Explained
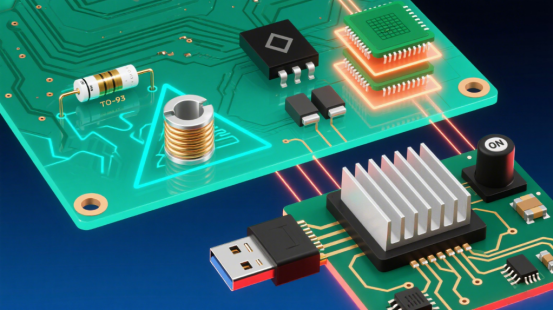
Figure 1: Key Printed Circuit Board Components
Printed circuit boards, or PCBs, are the heart of almost every electronic device we use today. From smartphones and laptops to home appliances, these boards connect all the important parts that make a device work.
But have you ever wondered what makes a PCB actually function? The answer lies in its components. Understanding printed circuit board components is key for anyone who wants to design, build, or even repair electronic devices.
In this article, we will explain the most important PCB components, from resistors to integrated circuits, showing how each part plays a role in making electronics work smoothly and reliably.
What Are Printed Circuit Board Components?
Printed circuit board components, or PCB components, are the parts that make a PCB work. In simple terms, they control, transfer, and process electrical signals inside an electronic device. Without them, a PCB is just a flat board covered with copper lines—it can’t do anything on its own.
PCB components are generally divided into three main categories: passive components, active components, and connectors & support components. Passive components don’t produce energy themselves but help control or store it. Active components can control the flow of electricity and amplify signals. Connectors and support components help connect the PCB to other circuits or devices and provide mechanical support.
In short, PCB components are the building blocks of electronic devices. Each part has a specific job, and together they allow electronics to perform complex tasks quickly and efficiently. Understanding these components is essential for anyone designing, repairing, or studying electronic devices.
Key PCB Components Explained
Electronic devices work because of their PCB components, and each part has a special role. Let’s look closer at the main types and see exactly how they make electronics work.
1. Passive Components
Passive components, like resistors, capacitors, and inductors, don’t generate electricity but are essential for controlling, storing, and filtering electrical signals.
l Resistors control how much current flows through a circuit. For example, in a smartphone, they prevent too much electricity from reaching sensitive chips, protecting them from damage. They also help divide voltage so components receive the correct power.
l Capacitors store and release small amounts of energy, which helps smooth out power supply and remove unwanted noise from signals. They are commonly used in power supplies, audio circuits, and filtering circuits in computers and TVs.
l Inductors store energy in a magnetic field and help filter high-frequency noise. They are often used in power converters, radio circuits, and devices that need stable current flow.
Together, passive components keep electricity safe, stable, and properly controlled, allowing devices to run reliably.
2. Active Components
Active components, including diodes, transistors, and integrated circuits (ICs), can control the flow of electricity, amplify signals, and process information.
l Diodes let electricity flow in only one direction, preventing damage from reverse current. They are used in chargers, LEDs, and protection circuits.
l Transistors act like electronic switches or amplifiers. They can turn a circuit on or off, or make a weak signal stronger. For instance, in a radio or smartphone, transistors amplify audio or data signals so the device works correctly.
l Integrated Circuits (ICs) combine hundreds or thousands of tiny components into a single chip that handles complex tasks, like signal processing, logic control, or memory storage. ICs are found in almost every modern device, from computers and phones to IoT devices.
Active components make modern electronics smart, fast, and capable of complex operations.
3. Connectors & Support Components
Connectors and support components help a PCB connect to other circuits, manage power, and stay physically stable.
l Connectors transmit signals and power between the PCB and other boards or devices. Examples include USB ports, HDMI connectors, and battery terminals.
l Switches allow users to control circuits, such as turning a device on or off, or selecting different modes in electronics.
l Heat sinks and mounting supports prevent overheating and keep components securely in place. Heat sinks are critical in computers, power electronics, and LED lights, where components generate a lot of heat. Mounting supports protect the PCB from vibration and shock, especially in industrial machines and vehicles.
Without these components, even a well-designed PCB cannot operate safely or reliably, no matter how advanced the circuits are.
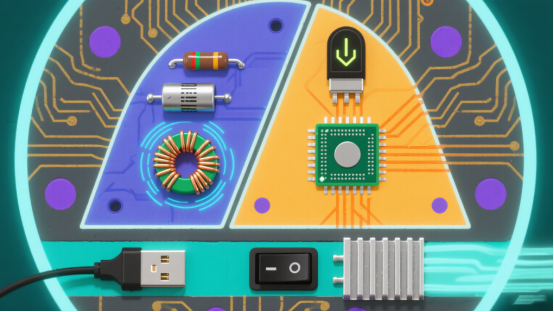
Figure 2: Key Printed Circuit Board Components: Passive Components, Active Components and Connectors & Support Components
How to Choose and Use PCB Components
Now that we’ve explored the main types of PCB components and how they work, the next step is learning how to pick the right parts for your project. Choosing the right components is key to making sure your device works well, lasts long, and stays safe.
1. Choose Components Based on Your Design Needs
Start by looking at what your device is supposed to do. For example, if you are building a small wearable device, you need tiny, low-power components. For a high-performance computer, you might need faster ICs and heat-resistant parts. Always match the component to the function it will perform in the circuit.
2. Pay Attention to Specifications
Every component has specific ratings for voltage, current, and power. Using the wrong rating can cause the component to fail or even damage your PCB. For instance, a resistor rated for too low a power level may overheat, or a capacitor with the wrong voltage limit may break down. Checking these specifications carefully is an essential part of PCB component selection.
3. Consider Materials and Reliability
Some components are made from materials that handle heat or stress better than others. For example, high-quality ICs or capacitors last longer and perform more reliably in demanding environments. Think about the temperature, vibration, and lifespan requirements of your device when choosing components. High-reliability parts are especially important in medical, industrial, or aerospace electronics.
4. Follow Best Practices for Use
Once you have selected the right components, make sure to install them correctly. Pay attention to orientation, soldering quality, and placement on the PCB. Using components properly ensures your circuit works safely and efficiently.
In short, choosing the right PCB components is about matching your design needs, checking specifications, considering materials, and using parts correctly. Doing this carefully will help your device perform better, last longer, and avoid costly failures.
Conclusion
Printed circuit board components are the building blocks that make electronic devices work. From resistors and capacitors to ICs and connectors, each component has a specific role that keeps the device running smoothly, efficiently, and safely.
Understanding and choosing the right PCB components is essential for anyone designing, repairing, or studying electronics. Picking the right parts not only improves performance but also ensures reliability and longevity, whether it’s a smartphone, a computer, or an industrial device.
If you want to learn more about PCB components or need help selecting the right parts for your project, check out PCB MASTER, a trusted supplier and expert in printed circuit boards. Their team can guide you through the process and make sure your electronics work the way they should.
FAQs
1. Why do some PCB components look very small?
Many PCB components are very tiny because modern electronic devices, like smartphones, smartwatches, and tablets, need to be compact and lightweight. Small components save space, allowing engineers to fit more features into a smaller device. Despite their small size, these components perform the same functions as larger ones. For example, a tiny surface-mount resistor can control current just like a bigger through-hole resistor. Engineers also carefully design the PCB layout so that even with small parts, the device doesn’t overheat or fail, keeping it reliable and efficient.
2. Can I use any type of component on a PCB?
No, each component is designed for a specific purpose, and not all components are interchangeable. Components have ratings for voltage, current, and power, which must match the circuit’s requirements. Using a resistor with too low a power rating could overheat, or a capacitor with the wrong voltage rating could fail and damage other parts. Choosing the right component involves reading datasheets, understanding how the part interacts with the rest of the circuit, and sometimes testing it in a prototype. Correct selection is essential for safe, reliable, and long-lasting electronics.
3. How do connectors help PCBs in real devices?
Connectors are like bridges that allow PCBs to communicate with other boards, devices, or power sources. For example, a USB connector on a phone not only provides power for charging but also allows data transfer to a computer. HDMI connectors transmit video and audio signals from a device to a display. Without connectors, a PCB could not send or receive signals, and the device would not function as intended. Connectors also make devices easier to repair or upgrade, since parts can be connected or replaced without soldering directly onto the PCB.
4. Why are heat sinks important for some PCB components?
Some PCB components, like integrated circuits (ICs) or power transistors, generate heat when operating. If this heat is not managed, it can cause the component to fail or shorten its lifespan. Heat sinks help draw heat away from the component, keeping it cool and allowing it to operate efficiently. For example, in a computer, the processor uses a heat sink to prevent overheating during heavy tasks. Similarly, LEDs in high-power lighting require heat sinks to maintain brightness and prevent damage. Proper heat management is crucial in industrial electronics, medical devices, and aerospace applications, where failure could be dangerous or costly.
5. How can learning about PCB components help me in electronics?
Understanding PCB components is the foundation for designing, repairing, and improving electronic devices. Knowing what each part does—like resistors controlling current, capacitors storing energy, or ICs processing information—helps you make better choices when building circuits. It also prevents mistakes, like using the wrong voltage or ignoring heat management, which could damage the device. Even a basic understanding allows you to troubleshoot problems, select the right replacement parts, or modify designs for better performance. In short, knowledge of PCB components makes electronics work safer, smarter, and more reliable.
