PCB Serial Numbers The Big Wisdom Behind a Small Identifier - Why It's So Important
Introduction
In modern electronics manufacturing, a serial number is like a PCB’s ID card, recording the unique life story of each circuit board. Serial numbering is the method used to uniquely identify and keep track of printed circuit boards throughout their lifecycle, supporting identification, traceability, and repair.
Imagine your smartphone develops a fault, and a technician scans a small code inside to trace that circuit board’s production batch, assembly time, and even test records. This seemingly simple code is the PCB serial number – an essential traceability tool in contemporary electronics manufacturing, and a key part of serial numbering for keeping track of individual boards from production to repair.
What is a PCB Serial Number?

A PCB serial number, short for Printed Circuit Board serial number, is a unique identifier assigned to each circuit board or circuit board assembly to uniquely identify individual boards. Like a human fingerprint, no two serial numbers are identical, enabling manufacturers to precisely identify and track the entire lifecycle of every single PCB. Each board is assigned a unique serial number.
From simple numeric combinations to complex QR codes, from direct silkscreen printing to laser engraving, the forms of serial numbers vary widely, but their core purpose remains constant: enabling precise traceability. Serial numbers may include letters as well as numbers to encode additional information, such as manufacturer details or production batches.
Basic Composition of a Serial Number
A typical PCB serial number usually includes:
·Production date and batch code
·Date code
·Purchase date
·Production line identifier
·Product model and version
·Supplier information
·Unique sequence code
This information is combined according to specific encoding rules, forming a compact yet information-rich identifier. Serial numbers can encode specific details such as manufacturing data, purchase date, and may be linked to design files like gerber files for enhanced traceability. Some boards may have two part numbers: one for the bare board and a second part number for the fully assembled board, both referenced in the serial numbering system.
Locating the Serial Number

Finding the serial number on a circuit board is a crucial first step for anyone needing to quickly identify a board and access its production information. Serial numbers are typically printed or etched directly onto the board’s surface, but their exact location can vary depending on the manufacturer and the board’s design. Common places to look include near the part number, along the ground plane, or adjacent to large wiring traces. Sometimes, the unique code may be tucked away in less obvious spots, requiring a careful inspection—using a magnifying glass can be especially helpful for spotting small or faint markings.
In some modern circuit boards, the serial number isn’t just written on the surface; it may be stored electronically in a memory chip. In these cases, retrieving the serial number data requires a serial data communication program to read the information directly from the chip. Whether physically printed or digitally stored, the serial number serves as the key to unlocking the board’s production data, such as manufacturing details and specific part numbers. By accurately locating and identifying this unique code, users and technicians can streamline the identification process, making repairs, upgrades, and maintenance more efficient and reliable.
Various Marking Methods for PCB Serial Numbers
Traditional Silkscreen Printing

Silkscreen printing is one of the earliest technologies used for PCB serial number marking. Similar to traditional printing, it transfers ink onto the PCB surface through a stencil. This method typically produces written serial numbers, which are easy to read but have limitations in data capacity and automation compared to bar codes. This method is low-cost and suitable for high-volume production, but has limited resolution, and the marking can wear off or fade over time.
Laser Engraving/Marking

Laser engraving is currently the mainstream method for serial number marking. It uses a high-energy laser to ablate a permanent mark onto the PCB surface. Manufacturers often etch serial numbers onto prominent features such as the ground plane or large wiring trace for better visibility and durability. Markings created this way cannot be easily altered, are resistant to high temperatures and chemical corrosion, and involve no physical contact with the PCB surface, avoiding mechanical damage.
QR Codes and Barcodes

With increasing traceability demands, traditional numeric serial numbers have gradually evolved into QR codes and barcodes. Bar codes are widely used for PCB identification because they can store more data than traditional serial numbers, including manufacturing parameters such as flux density. These high-density information carriers can store large amounts of data in a very small space and are easily read quickly by automated equipment, significantly improving traceability efficiency on production lines. A single scan of a barcode can provide quick access to all relevant information about a board, making the data easily accessible during manufacturing and repair.
Why Are PCB Serial Numbers So Important?
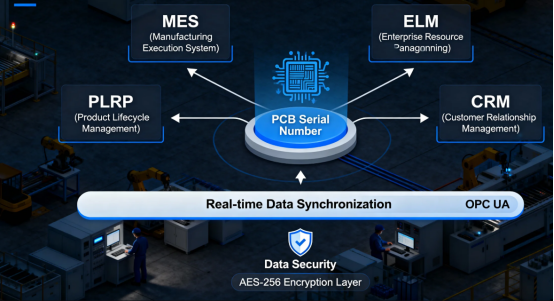
The Core Pillar of Quality Control
In the electronics manufacturing industry, quality is paramount. PCB serial numbers provide the foundation for traceability in quality control. Each unique serial number identifies a specific board and is used for verification during quality checks, ensuring that every item can be tracked and authenticated throughout the manufacturing process.
When a quality issue arises in a product batch, serial numbers enable:
·Rapid identification of the affected product range
·Tracing back through each step of the production process
·Analyzing the root cause of the problem to prevent recurrence
·Implementing precise recalls, minimizing financial losses
A renowned automotive electronics supplier once used PCB serial numbers to identify a batch of control modules with potential failure risks within 24 hours, avoiding a large-scale recall and saving millions of dollars in costs.
Meeting Compliance and Industry Standards
In high-reliability sectors like medical, aerospace, and automotive electronics, product traceability is not an option but a mandatory requirement.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for medical devices and the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) for avionics have clear traceability requirements. PCB serial numbers help manufacturers meet these regulatory demands, providing necessary compliance evidence. Consulting the manufacturer's guide can help locate serial numbers and ensure compliance with industry standards.
Optimizing Production Processes
Serial numbers are not just product identifiers; they are also recorders of the production process. By analyzing production data linked to serial numbers, manufacturers can:
·Identify production bottlenecks
·Optimize equipment utilization
·Improve production line balance
·Reduce material waste
Manufacturers store serial numbers and production data in integrated circuits or memory chips on the board, allowing for efficient data retrieval and process optimization.
These data-driven optimizations help companies enhance production efficiency and lower manufacturing costs.
Strengthening Supply Chain Management
In the globalized electronics industry, supply chains are increasingly complex. PCB serial numbers act as an information link connecting various stages of the supply chain, enabling manufacturers to:
·Track material sources
Circuit card assembly (CCA) numbers and purchase date information are also used to enhance inventory management and traceability throughout the supply chain.
·Monitor inventory turnover
·Optimize procurement plans
·Prevent counterfeit products
Especially when dealing with sudden supply chain disruptions (like the chip shortage during the pandemic), a serial number system can help companies quickly adjust production plans and prioritize the supply of critical products.
After-Sales Service and Warranty Management
Once a product enters the market, PCB serial numbers play a vital role in after-sales service and warranty management. Service personnel can scan the serial number to:
·Verify product authenticity
·Confirm warranty status
·Access technical documentation
·Record service history
In addition to the serial number, service personnel may also reference the CCA number and date code to verify warranty status and access detailed service records. The date code helps identify the manufacturing date of the product, while the CCA number, often found on the circuit board or stored in firmware, serves as a unique identifier for more precise tracking.
This not only improves service efficiency but also enhances customer experience and brand loyalty.
Best Practices for PCB Serial Number Implementation

Balancing Clarity and Durability
Serial numbers must be clearly readable while withstanding various challenges encountered during PCB assembly and in the use environment. Choosing the right marking technology and location is crucial, considering:
·Thermal stress (e.g., reflow soldering temperatures)
·Chemical exposure (e.g., cleaning agents)
·Mechanical stress (e.g., installation and vibration)
·Expected product lifespan—modern PCBs often use polyimide labels and advanced marking techniques to ensure both clarity and durability.
Standardized Encoding System
Establishing a uniform and logical encoding system is key to successful serial number implementation. A good encoding system should:
·Avoid ambiguity and duplication
·Facilitate manual interpretation
·Support automated reading
·Be scalable
·Include letters in serial numbers to help avoid ambiguity and support a scalable encoding system
End-to-End Integration
The serial number system should be fully integrated with the company’s ERP, MES, QMS, and other systems, enabling full lifecycle management from design to end-of-life. This integration ensures data consistency and real-time availability, providing reliable support for decision-making. Integrating off the shelf solution RFID chips can also provide real time alerts for tracking and management.
PCB Serial Number Security
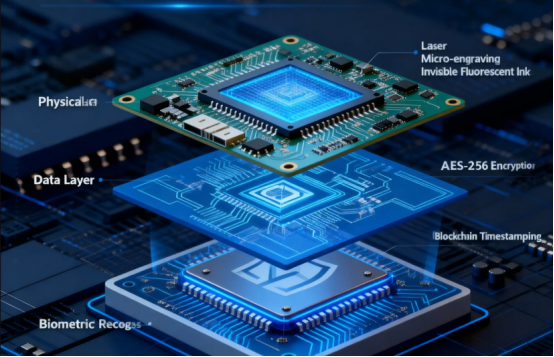
Ensuring the security of PCB serial numbers is a critical component of effective inventory management and quality control. Serial numbers are not just identifiers—they are essential for tracking and verifying the authenticity of circuit boards throughout their lifecycle. To protect this vital serial number data, manufacturers employ a range of security measures. Encryption is often used to safeguard serial numbers stored in memory chips, making it much harder for unauthorized parties to access or alter production information.
Advanced barcode systems and RFID chips add another layer of protection, allowing for secure, automated tracking of pcb serial numbers and making it significantly more difficult for counterfeiters to replicate or tamper with serial numbers. These technologies are especially important in the consumer electronics industry, where the use of counterfeit boards can pose serious safety risks. By implementing robust serial number security protocols, manufacturers not only protect their intellectual property but also ensure that only genuine boards are used in production and distribution. This commitment to security is critical for maintaining trust, ensuring product quality, and supporting efficient data-driven inventory management.
Troubleshooting
When it comes to troubleshooting circuit boards, the serial number is often the technician’s best friend. By identifying the serial number on a board, technicians can instantly access a wealth of production information, including the manufacturing date, batch number, and a list of electronic components used. This detailed data allows for targeted diagnostics, helping to pinpoint potential issues more quickly and accurately.
In many cases, the serial number also provides access to valuable test data and modification status records, offering insights into the board’s history and any changes made during its lifecycle. This information is crucial for identifying the root cause of problems and ensuring that repairs are both effective and efficient. Additionally, verifying the serial number helps confirm the authenticity of the board, ensuring that only genuine components are used in the repair process.
Serial numbers also play a key role in managing warranty periods. By referencing the serial number, technicians can confirm whether a board is still under warranty and ensure that repairs are performed within the appropriate timeframe, reducing the risk of invalidating coverage. Overall, integrating serial numbers into the troubleshooting process streamlines workflow, minimizes downtime, and enhances the reliability of repair operations for all types of circuit boards.
Future Development Trends
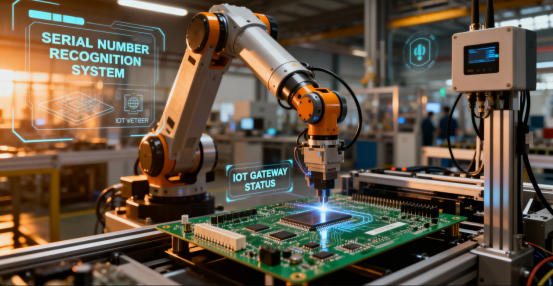
Integration with the Internet of Things (IoT)
With the development of IoT technology, PCB serial numbers are merging with smart sensors and connectivity technologies, enabling real-time condition monitoring and predictive maintenance. Integrating an RFID chip allows for real-time updates and automatic tracking of PCB status. Future PCBs might not only identify themselves but also report their own health status and usage environment.
Application of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain provides an immutable, distributed ledger for PCB serial numbers, greatly enhancing supply chain transparency and trustworthiness. By recording key events on the blockchain, all participants can verify the authentic history of a product, effectively combating counterfeits.
Artificial Intelligence and Big Data Analytics
Artificial intelligence is transforming how we utilize serial number data. By analyzing vast amounts of data linked to serial numbers, AI systems can:
·Predict equipment failures
·Optimize maintenance schedules
·Identify potential quality risks
·Automatically adjust production parameters
These intelligent applications will further amplify the value of serial numbers, driving electronics manufacturing towards higher levels of intelligence.
Conclusion
The PCB serial number, this seemingly insignificant mark, is actually an invisible pillar of modern electronics manufacturing. It is not only a guardian of product quality but also a compass for production optimization and a vital link connecting various stages of the supply chain.
In today's world of increasingly complex electronic products and ever-higher quality requirements, investing in a robust serial number management system is no longer a choice but a prerequisite for sustainable business development. Regardless of company size, a well-designed and properly implemented serial number system will yield substantial returns on investment, providing a unique competitive advantage in the fierce market.
When we examine an ordinary PCB, that small serial number carries within it the wisdom and precision of the entire modern electronics manufacturing industry – it is small yet crucial, simple yet profoundly significant.
FAQs
Q. Must all PCBs be printed with a serial number?
A. Not all, but it is a hard requirement in critical fields. Compliance industries such as automotive and medical (requiring IATF 16949, ISO 13485 certification) mandate serial numbers for full-process traceability; low-cost, consumer-grade PCBs (e.g., in toys) might omit them, but having a serial number facilitates better quality control.
Q. Can serial numbers only be numbers?
A. No. They are mostly alphanumeric (e.g., "SH2310-B5-7891A"), and some include symbols. The core requirement is to ensure "each unit is unique," rather than being limited to a pure numeric format.
Q. What is the core purpose of a serial number on a PCB?
A. Primarily four points: Meeting industry compliance requirements; precisely locating faulty batches to reduce recall costs; tracing production/repair history; and assisting in verifying product authenticity and warranty status.
Q. What are the common printing processes for serial numbers?
A. Laser etching (durable, suitable for high-temperature environments); UV inkjet (low cost, suitable for consumer electronics); chemical etching (highly durable, used in aerospace). The choice depends on the application.
Q. What is the relationship between a serial number and a QR code/barcode?
A. QR codes/barcodes are the "machine-readable form" of the serial number. Scanning them allows for quick data reading (avoiding manual entry errors). They are often printed alongside the text serial number, especially suitable for batch tracing.
Q. Why might a PCB have multiple serial numbers?
A. Usually to meet different scenario requirements: For example, a military PCB might have one number for government inventory tracking and another for commercial compliance; secondary suppliers might also add additional serial numbers for after-sales maintenance.
Q. What if the serial number is damaged and unreadable?
A. Clues can be pieced together using information like the PCB model, manufacturing date, and place of origin. Alternatively, contact the manufacturer, who can potentially reverse-match the corresponding serial number using batch records.
Q. What should be considered when customizing a serial number?
A. It must contain a unique identifier and can include codes for batch/place of origin; placement should avoid functional areas like solder pads; QR codes require a 2mm quiet zone. Once confirmed, serial numbers cannot be changed, and each unit must have a unique one.
Q. Can a serial number directly prove a PCB is genuine?
A. It can assist verification but is not absolute. Genuine serial numbers allow querying production records through the manufacturer's system. If the serial number is duplicated, has an abnormal format, or fails verification, it might be counterfeit.
Author: Jack Wang
