Top Benefits of PCB Via with Resin Filling Techniques
Introduction
Resin-filled vias in PCBs, specifically the pcb via with resin, prevent air and liquid traps, boosting reliability and performance. This article explores their benefits, types, and manufacturing processes.
Key Takeaways
·Resin plug holes enhance PCB reliability by preventing air and liquid trapping, improving mechanical strength and electrical conductivity.
·Two main types of resin plug holes exist: conductive, which enhances electrical properties, and non-conductive, which supports structural integrity without affecting electrical functionality.
·Advanced techniques like vacuum resin plugging improve the quality and performance of resin fillers in HDI PCBs, addressing common issues such as air entrapment.
Understanding Resin Plug Holes in PCBs
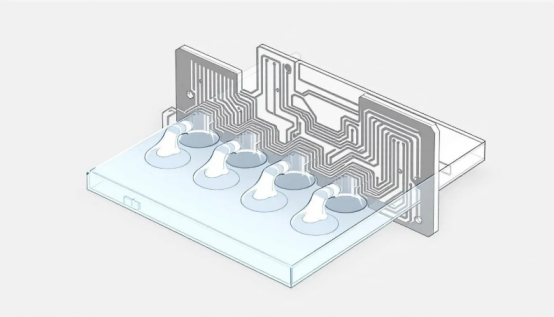
A resin plug hole in a PCB is a filled hole with epoxy resin, often electroplated with copper for sealing. These holes enhance the reliability of PCBs by reducing the risk of trapped liquid or air, which can compromise the board’s functionality.
Knowing the evolution and application of resin plug holes helps in appreciating their role in modern electronics.
History of Resin Plug Holes
The journey of resin plug holes began with green oil plug holes, which were the initial standard for filling vias in PCBs. However, these were prone to quality issues such as shrinking and bubble formation. To address these problems, a Japanese company developed a type of resin suitable for via-hole filling, which significantly improved the process.
Resin materials and epoxy resins are now widely used in various modern consumer electronics applications.
Why Use Resin Plug Holes?
Resin plug holes enhance PCB reliability by preventing air or liquid trapping, which can lead to failures. Filling vias also improves electrical conductivity and mechanical strength, making the boards more robust and efficient. The via-fill plug technique is particularly beneficial when electrical conductivity is not critical, as it provides necessary insulation.
In PCB design:
·Filled and capped vias reduce the signal path length compared to traditional bga designs.
·Placing vias on component pads further shortens signal paths.
·This approach is essential for dense BGA connections where traditional designs struggle with close ball proximity.
Resin plug holes are vital for fabricating multi-layered circuit boards, particularly in via-in-pad applications. This technique boosts the performance and reliability of HDI PCBs, making them indispensable in modern electronics. Additionally, the use of pcb resin plug holes enhances the overall integrity of the design.
Types of Resin Plug Holes in PCBs
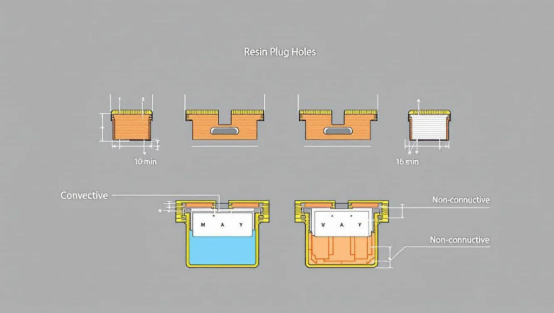
Resin plug holes can be broadly categorized into two types: conductive and non-conductive. Conductive resin plug holes use materials like silver or copper paste to enhance electrical conductivity, while non-conductive resins provide structural support without affecting electrical properties.
Knowing these types aids in selecting the appropriate filling method for specific PCB applications.
Conductive Resin Plug Holes
Conductive resin plug holes utilize conductive materials like conductive copper and epoxy to enhance electrical conductivity in PCBs. These materials offer better thermal conductivity compared to alternatives like silver epoxy.
The filling process involves using thermally curable resins like TAIYO THP-100 DX1, and sealing the top with techniques such as immersion or electroplated copper. This not only improves conductivity but also minimizes issues like voids, leading to better reliability in PCB designs.
Non-Conductive Resin Plug Holes
Non-conductive resin plug holes provide structural support to pads in via-in-pad designs without compromising electrical properties. Epoxy paste or resin is commonly used to fill regular vias in non-conductive via plugging. However, avoiding voids is crucial as they can create connectivity issues.
Type III (a) via filling may trap air or solvent, leading to problems during the curing process.
Manufacturing Process for Resin Plug Holes
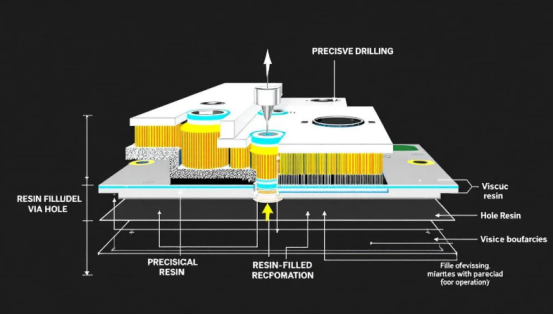
The manufacturing process for resin plug holes is intricate and requires precision at every step in the resin process. It typically involves:
·Drilling
·Cleaning
·Resin filling
·Planarization
·Electroplating
Each stage is crucial to ensure high yield and performance of the PCBs, making the processed process both challenging and essential for quality assurance, with multiple layers involved.
Drilling and Cleaning Via Holes
Drilling is the first step in the process of filling vias. Selecting which vias to fill is done using the Drill editor. If all via holes are to be filled, data can be sent normally with the fill vias option selected, provided that the vias are drilled.
After drilling, a cleaning method using a brush and solvents is applied to ensure the holes are free of debris. This step is critical to prevent closed vias from compromising the PCB’s functionality.
Resin Filling and Planarization
The preferred resin for filling via holes is TAIYO THP-100 DX1, known for its thermal curing properties. Applying a proper vacuum during the resin filling process minimizes bubble formation, ensuring a stable fill. A slow filling rate also helps reduce air entrapment, which leads to bubbles.
Resin plug holes help reduce the risk of voids in the dielectric material, which is particularly important in high-density boards. Completely filling vias before soldering prevents tin leakage.
Electroplating and Final Finishing
An electroplated copper pad cap provides a smooth surface and prevents tin leakage for resin plug holes. Though this extra plated step adds to manufacturing costs, it ensures high-quality resin plug holes that are durable during assembly and operation.
Advanced Techniques in Resin Plugging

Advanced techniques like vacuum resin plugging and specialized methods for HDI PCBs further enhance PCB reliability and performance. These modern methods address common issues like air entrapment and are essential for high-density electronic designs.
Vacuum Resin Plugging
Vacuum resin plugging uses vacuum technology to ensure stable resin plugs by minimizing air bubbles during the filling process. This technique requires a vacuum laminator for effective sealing, enhancing the reliability of the resin plugs.
Resin Plugging for HDI PCBs
Resin plugging for HDI PCBs involves specific techniques that accommodate the compact layout and higher component density of these boards:
·Microvias in HDI boards are filled through specialized plating tanks designed for bottom-to-top filling.
·This method maintains stability during lamination.
·It also prevents resin seepage.
Cost and Quality Considerations
Balancing cost and quality is vital in the resin plugging process. Material costs, manufacturing complexity, and quality control measures significantly impact both the expense and reliability of the final product.
Cost Factors in Resin Plugging
Material costs for via filling are directly proportional to the number of vias in a PCB design. The type of paste used is a crucial factor influencing the overall cost. Manufacturing complexity varies, affecting costs significantly between conductive and non-conductive filling methods.
Factors impacting the choice of via-filling include the board’s cost and production time.
Ensuring Quality in Resin Plug Holes
Quality control for conductive-filled vias involves:
·Rigorous testing to verify electrical conductivity.
·Electroplating to provide a protective layer over resin-filled vias, ensuring durability during assembly and operation.
·Using high-quality resin formulations to reduce the likelihood of tin leakage during soldering.
Moreover, applying proper flux before soldering can significantly reduce the risk of tin leakage.
Applications of Resin Plug Holes in Modern PCBs
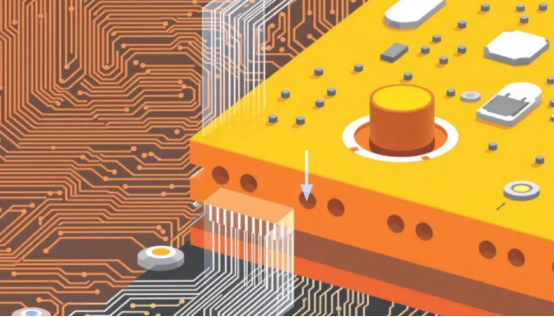
Filling vias holes in PCBs increases their mechanical strength, electrical conductivity, and thermal performance. Resin plug holes are pivotal in enhancing the reliability of PCBs by preventing moisture and air entrapment.
This technique supports modern electronic designs, particularly in space-constrained devices.
Resin Plug Holes in High-Density Circuit Boards
Resin plug holes are crucial for compact, multi-layer circuit boards, enhancing overall performance and reliability. Their key features include:
·Meeting thin dielectric layer design requirements, essential for HDI boards.
·Staying intact in blind microvias with dielectric thicknesses exceeding 0.5mm.
·Ensuring robustness in HDI plug holes.
These holes also help in thinning the inner layers dielectric layer thickness, important in high-density applications. One advantage of HDI blind hole plug holes is that they prevent zero copper on the pad after pressing, thereby enhancing the board’s quality.
Use in SMT Assembly
In SMT assembly, resin plug holes enhance mechanical strength, promoting better component durability. They prevent component misalignment during the soldering process.
Common Issues and Solutions in Resin Plugging
Common problems in resin plugging include shrinkage and bubble formation due to inadequate filling. Another concern is the risk of short circuits when vias are plugged and closely assembled with metal components.
Addressing these reliability issues is critical to maintaining the integrity and performance of PCBs.
Addressing Bubble Formation
To reduce and remove bubbles in resin:
·Warm the resin before mixing to help reduce bubble formation during pouring.
·Mix deliberately to minimize air bubble introduction compared to vigorous mixing.
·Use a heat source like a heat gun to effectively pop bubbles in the resin.
Preventing bubble formation is crucial to ensure high-quality resin plugs in PCB manufacturing.
Preventing Tin Leakage
If vias are not fully plugged, tin beads may remain in the hole, leading to solder defects. Completely filling tented vias before soldering prevents tin leakage and maintains the integrity of the soldering process.
Summary
Summarizing the key points discussed, resin plug holes are indispensable in modern PCB design and manufacturing. They enhance reliability, electrical conductivity, and mechanical strength, addressing common issues and supporting advanced applications in high-density and space-constrained electronic devices. The balance between cost and quality, along with the adoption of advanced techniques, ensures the optimal performance of PCBs. Embracing these methods will pave the way for innovation and excellence in the electronics industry.
FAQs
Q.What is a resin plug hole in PCB manufacturing?
A.A resin plug hole in PCB manufacturing is a filled hole using epoxy resin, typically electroplated with copper, which enhances the reliability and performance of the circuit board by preventing air or liquid entrapment.
Q.Why did the industry shift from green oil plug holes to resin materials?
A.The industry shifted from green oil plug holes to resin materials due to quality concerns such as shrinking and bubble formation. Resin materials effectively address these issues and have become the preferred choice.
Q.What are the main types of resin plug holes?
A.The main types of resin plug holes are conductive resin plug holes, which utilize materials like copper paste for enhanced electrical conductivity, and non-conductive resin plug holes, designed to provide structural support without impacting electrical properties.
Q.How does vacuum resin plugging improve the quality of resin plug holes?
A.Vacuum resin plugging significantly enhances the quality of resin plug holes by minimizing air bubbles during the filling process, resulting in more stable and reliable resin plugs. Utilizing a vacuum laminator during this technique ensures effective sealing.
Q.What are the common issues in resin plugging, and how can they be addressed?
A.Common issues in resin plugging, such as bubble formation and tin leakage, can be effectively addressed by warming the resin before mixing, deliberately mixing to eliminate air pockets, and ensuring complete filling of vias prior to soldering to prevent tin leakage. Implementing these practices will enhance the overall quality of the resin application.
Author: Jack Wang
