Choosing the Best PCB Colour for Your Project A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
When you look at a printed circuit board, the first thing that catches your eye is its color. That colored layer covering the PCB surface is called the solder mask, and while many think it's just for appearance, it serves crucial functional purposes that significantly impact your board's performance, manufacturability, and cost.
PCB solder mask color selection is more than just an aesthetic choice—it's a technical decision that affects inspection accuracy, thermal management, production yield, and even the final product's market perception. Whether you're designing consumer electronics, industrial equipment, or high-reliability medical devices, understanding solder mask colors can help optimize your design and manufacturing process.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore everything you need to know about PCB solder mask colors, from their technical characteristics to design considerations, cost implications, and production timelines.
What is Solder Mask and Why Does Color Matter?
Solder mask, also known as solder resist, is a thin lacquer-like layer of polymer applied to the copper traces of a PCB. Its primary functions include:
·Preventing solder bridges between closely spaced components
·Protecting copper traces from oxidation and environmental damage
·Providing electrical insulation between conductors
·Enhancing contrast for component placement and inspection
In addition to these functions, the choice of pcb colors (or pcb colour) plays a significant role in both the appearance and functionality of the pcb board. The color selected can impact visual clarity, inspection ease, and even the branding of the final product.
The color of the solder mask affects several practical aspects of PCB manufacturing and use. Solder mask ink and solder mask colour are important considerations in pcb board manufacturing, as they influence protection, visibility, and branding.
Selecting the right color for pcb boards is a key part of the design and manufacturing process.
Visual Inspection and Repair
Different colors provide varying levels of high contrast with components and solder joints, directly impacting the ease of manual inspection and the ability to visually inspect and rework the board. This becomes particularly important for boards with fine-pitch components or complex assemblies.
When there is high contrast between the solder mask and the components, component identification during assembly and maintenance is much easier.
Additionally, the contrast between traces and empty space or empty spaces on the PCB helps technicians visually inspect and repair the board more efficiently.
Thermal Management
Darker colors tend to absorb more heat during the soldering process, and this increased heat absorption can affect the operating temperature and thermal performance of the PCB, while lighter colors reflect it. This thermal characteristic can influence soldering quality and component temperature during operation.
Light Reflection
In optical applications or devices with LED indicators, solder mask color can affect light reflection and absorption properties. Glossy solder mask finishes tend to reflect light directly, which can make it easier to inspect the board under harsher light conditions, while matte finishes are less reflective and may be preferable when there is less light available for inspection.
Common PCB Solder Mask Colors and Their Characteristics

Green: The Industry Standard
Characteristics:
·Most common color (approximately 70-80% of all PCBs)
·Excellent contrast with white silkscreen
·Optimal for automated optical inspection (AOI)
·Well-established manufacturing processes
·Green PCBs are known for providing the highest contrast between traces and empty spaces, which aids in inspection and repair.
·The standard pcb color code (color code) for green solder mask is widely referenced in manufacturing.
Applications:Green PCB is the industry standard for readability and inspection, making it the default choice for most consumer electronics, industrial controls, and general-purpose applications. Its widespread use means manufacturers have extensive experience with it, resulting in consistent quality.
Advantages:
·Lowest cost due to economies of scale
·Highest manufacturing yield
·Best compatibility with all PCB processes
·Excellent contrast for inspection, especially due to the highest contrast between traces and empty spaces on green PCBs
Disadvantages:
·Common appearance (may not stand out for premium products)
·Limited aesthetic differentiation
Blue: The Professional Choice
Characteristics:
·Darker than green but still provides good contrast
·Popular for high-end consumer products
·Gives PCBs a “professional” look
·Blue PCB and blue solder mask are commonly used for their professional appearance and good contrast
Applications:Frequently used in graphics cards, industrial equipment, and premium consumer electronics where aesthetic differentiation is desired without sacrificing inspectability. Arduino boards often use blue solder mask to improve visibility and aesthetics. Blue solder mask does not produce bright background colors or sharp contrasting edges, making it suitable for display and LCD applications.
Advantages:
·Good contrast with white silkscreen
·perceived as more premium than green
·Widely available without significant cost premium
Disadvantages:
·Slightly higher cost than green (typically 5-10% premium)
·May absorb slightly more heat during soldering
Red: The High-Visibility Option
Characteristics:
·Bright color that provides excellent contrast
·Popular for development boards and demonstration units
·Creates a striking visual appearance
·Red PCB and red solder mask are chosen for their bold appearance and are often used to distinguish specific boards.
·Red solder masks provide good contrast for silkscreen and make flux residues easier to identify and clean during inspection.
Applications:Often chosen for evaluation boards, educational kits, and products where visual appeal is important. Red solder masks are also used to help with silkscreen visibility and flux residue management. Some studies suggest red PCBs are perceived as “faster” or “higher performance” by consumers.
Advantages:
·Excellent visibility for inspection and debugging
·Aesthetically distinctive appearance
·Good market perception for performance products
·Red solder masks offer clear silkscreen visibility and aid in cleaning flux residues
Disadvantages:
·Higher cost than green (10-15% premium)
·May show scratches and imperfections more visibly
Black: The Premium Aesthetic
Characteristics:
·Provides a sleek, professional appearance
·Popular in high-end consumer electronics
·Lower contrast with traces and components
·Black pcb and black pcbs are favored for their premium look but can be challenging for inspection and heat management.
·Black solder mask and black solder masks enhance the visibility of large components and labeling, but require careful temperature monitoring during the reflow process to prevent discoloration.
·Black circuit boards are often chosen for their visual appeal and heat absorption properties in high-end products.
Applications:Widely used in premium smartphones, audio equipment, and luxury electronics where appearance matters. Often paired with gold plating for enhanced visual effect.
Advantages:
·Premium aesthetic appeal
·Hides copper traces well for clean appearance
Disadvantages:
·Highest cost among standard colors (15-30% premium)
·Difficult inspection and debugging due to low contrast
·Absorbs more heat during soldering process
·Shows dust and fingerprints easily
White: The LED-Friendly Option
Characteristics:
·Maximizes light reflection for LED applications
·Provides clean, modern appearance
·Shows contamination easily
·White solder mask and white solder masks are chosen for their high reflectance, but they present challenges in cleaning and can be difficult to visually inspect due to low contrast with copper traces.
·White pcb and white pcbs are often used for their clean, modern appearance in consumer electronics and medical devices.
·The silkscreen layer on white solder masks can provide high contrast for artwork, but it may still be difficult to visually inspect fine details.
Applications:Ideal for products with LED indicators, backlighting, or optical sensors. Commonly used in lighting products, display technologies, medical devices, and white pcbs for consumer electronics.
Advantages:
·Excellent light reflection properties
·Clean, modern aesthetic
·Good contrast with black silkscreen layer
Disadvantages:
·Shows scratches and stains easily
·Higher cost (15-25% premium)
·Requires extremely clean manufacturing environment
·White solder masks can be difficult to visually inspect and clean due to low contrast and dirt visibility
Yellow: The Niche Choice
Characteristics:
·Bright, distinctive appearance
·Moderate contrast with components
·Less common in commercial products
Yellow solder mask and yellow PCBs are often selected for their high contrast and unique appearance, making them suitable for highlighting specific areas or improving readability.
Applications:Occasionally used in specialized industrial equipment or for specific branding purposes. Sometimes chosen for educational kits to make traces more visible. Yellow PCBs can also be used to draw attention to certain circuit areas or enhance visual contrast for easier inspection.
Advantages:
·Unique appearance for product differentiation
·Reasonable contrast for inspection
Disadvantages:
·Limited availability at some manufacturers
·Higher cost (15-20% premium)
·Not ideal for fine-pitch components
Purple and Other Custom Colors
Characteristics:
·Unique appearance for product differentiation
·Varying availability across manufacturers
·Typically special-order items
·Many PCB manufacturers offer a wide range of color options, including custom and special-order colors such as purple PCB and other colours for specific needs
Applications:Used primarily for branding purposes or special edition products. Purple PCB is a popular choice for custom builds, and other colours are available for branding and differentiation. Purple has gained some popularity in gaming peripherals and custom PC builds.
Advantages:
·Maximum product differentiation
·Brand alignment through color matching
Disadvantages:
·Highest cost (25-50% premium)
·Limited manufacturer availability
·Potential quality consistency issues
·Longer lead times
Design Considerations for Solder Mask Color Selection

Inspection Requirements
Consider how the board will be inspected during manufacturing and debugging:
·Green and blue provide the best contrast for automated optical inspection (AOI)
·Black and dark blue make manual inspection more challenging
·Lighter colors (white, yellow) show solder joints more clearly
Thermal Management
The solder mask color affects thermal performance during soldering and operation:
·Dark colors (black, blue, green) absorb more infrared heat during reflow soldering
·Light colors (white, yellow) reflect heat and may require adjusted soldering profiles
·For high-power applications, color can influence component operating temperatures
Silkscreen Legibility
Ensure adequate contrast between solder mask and silkscreen colors:
·White silkscreen works well on dark colors (green, blue, black, red)
·Black silkscreen is necessary for light colors (white, yellow)
·Some color combinations (black on dark blue) may reduce legibility
Application Environment
Consider the end-use environment:
·Industrial environments may show dirt less on darker colors
·Medical and cleanroom applications often prefer light colors that show contamination
·Outdoor applications may benefit from UV-resistant formulations
Aesthetic and Marketing Considerations
The visual appearance matters for consumer products:
·Premium products often use black or custom colors
·Development boards frequently use bright colors for visibility
·Brand colors can be matched for product consistency
Manufacturing Considerations
Different colors have different manufacturing characteristics:
·Green has the most optimized process parameters
·Some colors may require additional curing time
·Certain pigments may affect exposure and development processes
Cost Implications of Solder Mask Color Choice
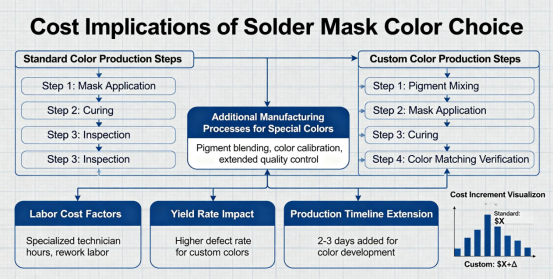
Material Cost Differences
The cost variation between solder mask colors comes from several factors:
·Pigment Cost: Some color pigments are more expensive to produce
·Demand Volume: Green is mass-produced, reducing cost
·Inventory Management: Special colors may require minimum order quantities
·Process Adjustments: Non-standard colors may require process changes
Typical Cost Premiums by Color
(Relative to standard green solder mask)
·Green: 0% (baseline)
·Blue: 5-10% additional cost
·Red: 10-15% additional cost
·White: 15-25% additional cost
·Black: 15-30% additional cost
·Yellow: 15-20% additional cost
·Custom colors: 25-50% additional cost
Additional Cost Factors
·Yield Impact: Some colors may slightly reduce manufacturing yield
·Inspection Time: Low-contrast colors may require longer inspection times
·Rework Costs: Difficult inspection may increase rework time and cost
·Minimum Order Quantities: Special colors may have MOQ requirements
·Lead Time Impacts: Custom colors may require longer procurement times
Production Cycle Time Considerations
Standard Colors (Green, Blue, Red)
·No significant impact on production timeline
·Typically readily available in inventory
·Standard curing and processing parameters
Non-Standard Colors (White, Black, Yellow)
·May add 1-2 days to production time
·Possible need for special ordering
·Process parameter adjustments needed
Custom Colors (Purple, Orange, Brand Colors)
·Can add 3-7 days to production timeline
·Often require minimum order quantities
·May need process development and validation
Quality Control Implications
·Familiar colors have established QC parameters
·New colors may require additional test panels
·Inspection systems may need calibration for different contrasts
Technical Performance Considerations
Electrical Properties
While all solder mask colors use similar base formulations, some differences exist:
·Dielectric Constant: Slight variations between colors (typically 3.0-3.5)
·Insulation Resistance: Generally consistent across colors
·Surface Insulation Resistance: Can be affected by pigment composition
Thermal Performance
·Heat Dissipation: Darker colors may radiate heat slightly better
·UV Resistance: Some pigments may degrade with UV exposure
·Thermal Stability: High-temperature stability varies slightly by formulation
Mechanical Properties
·Adhesion Strength: Generally consistent across colors
·Flexibility: Some pigments may affect flexibility in flexible circuits
·Abrasion Resistance: Color can affect visible wear characteristics
Specialized Solder Mask Types
Matte vs. Gloss Finish
·Matte Finish: Reduces glare, better for inspection under lighting
·Gloss Finish: Provides deeper color appearance, easier to clean
High-Temperature Formulations
Special formulations for lead-free soldering processes:
·Withstand higher reflow temperatures
·Available in limited color options
·May command premium pricing
Flexible Circuit Masks
Specialized formulations for flex and rigid-flex PCBs:
·Enhanced flexibility
·Typically available in standard colors only
·Higher cost than rigid PCB masks
UL-Recognized Masks
Certified for specific safety requirements:
·Different flame retardant ratings (94V-0, 94V-1, etc.)
·May have limited color options
·Documentation requirements
Industry Trends in Solder Mask Colors

Current Popularity
·Green: Still dominant for cost-sensitive and high-volume applications
·Black: Growing in premium consumer products
·Blue: Stable popularity in professional equipment
·White: Increasing with LED lighting and IoT devices
·Custom Colors: Growing demand for brand differentiation
Emerging Trends
·Color-Matching Services: Manufacturers offering custom color matching
·Regional Preferences: Different color preferences by geographic market
·Application-Specific Trends: Certain colors becoming associated with product categories
·Environmental Considerations: Development of more eco-friendly formulations
Best Practices for Solder Mask Color Selection
Prioritize Function Over Form
·Choose inspectability over aesthetics for complex boards
·Consider thermal requirements for high-power designs
·Evaluate environmental factors in end-use application
Consult with Your Manufacturer Early
·Inspection during manufacturing
·Debugging and rework during development
·Field service and repair requirements
·End-of-life recycling considerations
Consider the Entire Product Lifecycle
·Inspection during manufacturing
·Debugging and rework during development
·Field service and repair requirements
·End-of-life recycling considerations
Test Before Committing
·Request samples of different colors
·Evaluate under actual lighting conditions
·Test inspection systems with different colors
·Verify thermal performance if critical
Document Requirements Clearly
·Specify color precisely in design documents
·Include brand color references if matching
·Note any special requirements (matte/gloss, UL certification)
Conclusion
PCB solder mask color selection is a multifaceted decision that balances technical requirements, cost considerations, production factors, and aesthetic goals. While green remains the practical default for most applications, alternative colors offer opportunities for product differentiation and optimization for specific use cases.
The optimal color choice depends on your specific application:
·Cost-sensitive volume production: Green
·Premium consumer products: Black or blue
·LED and lighting applications: White
·Development and prototyping: Red or blue
·Brand-specific products: Custom colors
Remember that the most expensive option isn't always the best choice for your application. By understanding the trade-offs between different solder mask colors and consulting with your manufacturing partner early in the design process, you can make an informed decision that meets your technical requirements, budget constraints, and aesthetic goals.
Regardless of color choice, always prioritize manufacturability and inspectability to ensure the highest quality end product. The right solder mask color, combined with good design practices and a reliable manufacturing partner, will contribute significantly to the success of your electronic product.
Author: Jack Wang
