Blank Printed Circuit Board: Types, Materials, and Applications Explained
Open up an old phone, and you’ll spot a thin green board packed with copper lines—that’s the printed circuit board (PCB). Without it, your phone would be nothing more than an expensive paperweight. This little board is like the nervous system of your electronics, quietly making sure everything talks to each other.
But here’s the fun part: before it gets all those fancy components, it starts life as a blank printed circuit board—just a simple board with copper foil on top. Sounds boring? Not really. These blank boards are the foundation of every electronic device you love. In this guide, we’ll look at the different types of blank PCBs, what materials they’re made of, and where they’re used every day.
What Is a Blank Printed Circuit Board?
Okay, so what exactly is a blank printed circuit board? Imagine a pizza base before you add the cheese and toppings. That’s basically what a blank PCB is—a plain board with no components attached yet. It’s just the foundation, but without it, there’s no electronic “pizza.”
A blank PCB is usually made from an insulating material (like fiberglass) and covered with a thin layer of copper. The copper is where the magic happens—it forms the tiny pathways that electricity will travel through once the board is finished.
How Is It Different from a Regular PCB?
Here’s the big difference:
A regular PCB has all the components—chips, resistors, capacitors—soldered on it. It’s like a finished sandwich, ready to eat.
A blank PCB, on the other hand, is just the bread. No toppings yet. It’s the starting point before all the cool stuff gets added.
Why Is a Blank PCB So Important for Prototypes?
Engineers love blank PCBs when they’re testing ideas. Before building thousands of complex boards, they start with a blank PCB to design and check the circuit layout. It’s like sketching a plan before building a house—you want to make sure everything fits and works before committing to the real thing.
So, in short, a blank PCB board is the base, the starting point, and the quiet hero of every electronic device you use. Without it, nothing works. Pretty cool for something that looks so simple, right?
Types of Blank Printed Circuit Boards
Not all blank PCBs are the same. Just like pizzas come in different sizes and crust styles, blank PCBs come in different types too! Let’s look at the most common ones and why they matter.
1. Single-Sided PCB
This is the simplest kind of blank PCB. It has copper on only one side of the board. The other side is just plain insulation. Because of this, all the electronic paths stay on that one copper side, which makes it easy to design and cheap to make.
Where do we use it?
Simple gadgets like calculators
Power supplies
Basic toys
If your circuit isn’t complicated, this is your go-to blank PCB type.
2. Double-Sided PCB
Now we’re adding more room to play! A double-sided PCB has copper on both sides of the board. That means you can place components on the top and bottom and connect them using tiny holes called vias.
Why is this awesome?
You can fit more components in a smaller space
Great for slightly more advanced devices
Common uses:
Amplifiers
LED lighting systems
Industrial controls
3. Multilayer PCB
Here’s where it gets fancy. A multilayer blank PCB has three or more layers stacked together with insulation in between. It’s like a PCB sandwich! This type is perfect for high-density circuits where you need a lot of connections but don’t have much space.
Why do engineers love it?
Handles complex circuits
Reduces interference
Saves space
Where do you see it?
Smartphones
Computers
Medical equipment
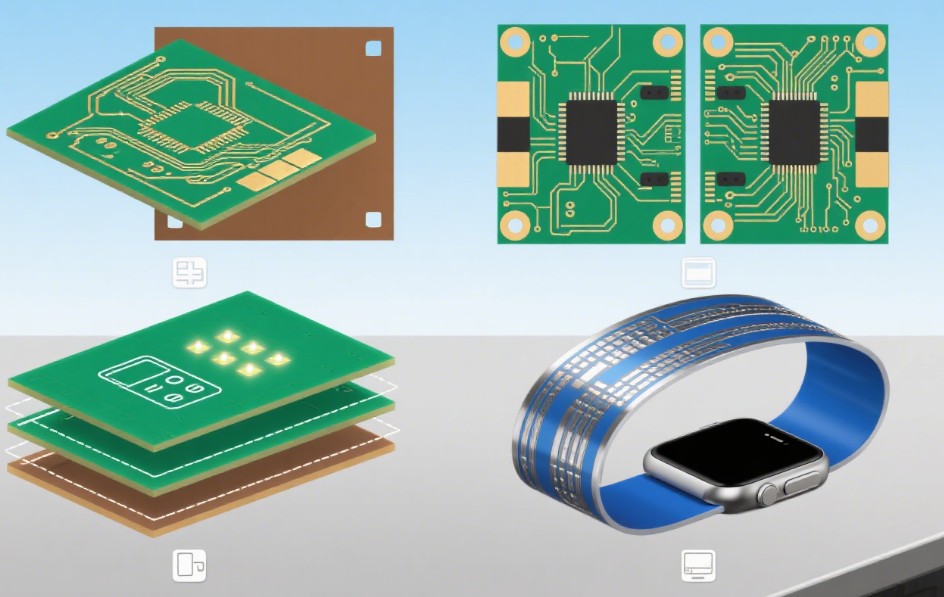
4. Flexible PCB
A flexible PCB can bend and twist without snapping. Unlike the stiff fiberglass used in regular boards, it’s made from materials like polyimide that allow it to move and fit into tight spaces.
Why is that useful?
Perfect for tight spaces
Great for devices that need to bend or fold
Examples:
Wearable electronics
Foldable phones
Automotive dashboards
Materials Used in Blank Printed Circuit Boards
Just like you can’t bake a pizza without dough, you can’t make a blank PCB without the right material. The material decides how strong the board is, how much heat it can handle, and even whether it can bend. Let’s look at the most common blank PCB materials.
1. FR4 (Fiberglass Epoxy)
Meet the superstar of PCB materials—FR4. This is the material you’ll find in most PCBs. It’s basically fiberglass soaked in epoxy resin, which makes it tough and stable.
Why is it popular?
Strong and durable (it doesn’t break easily)
Resists heat pretty well
Affordable for most projects
Where do we see it?
Consumer electronics (like your TV or remote)
Computers
Industrial boards
If you hear FR4 PCB board blank, think of the most common and reliable option for standard PCBs.
2. CEM-1 and CEM-3
These are like FR4’s cousins. They’re cheaper and used in simpler boards.
CEM-1
Made from paper and epoxy
Cheaper but less strong than FR4
Good for single-sided boards
CEM-3
A little better than CEM-1
Can be used for double-sided boards
Still not as strong as FR4, but more affordable
So, if cost matters more than performance, CEM materials might be the pick.
3. Metal Core (Aluminum or Copper)
This is the tough guy in the PCB family. Instead of fiberglass, the core is metal—usually aluminum. Why? Because it handles heat like a pro.
Why is it great?
Excellent heat dissipation
Perfect for high-power devices
Very durable
Where do we use it?
LED lighting (they get hot!)
Power converters
Automotive headlights
So if someone mentions metal core blank PCB, they’re talking about heavy-duty boards that can take the heat—literally.
4. Flexible Materials (Polyimide or PET)
These materials make flexible PCBs possible. Unlike rigid FR4, these are bendy and lightweight.
Why use flexible materials?
Great for tight spaces
Can fold without breaking
Light and thin
Where do we find them?
Foldable phones
Wearable electronics
Medical devices
If your project needs a PCB that twists and bends like a gymnast, polyimide or PET is the way to go.
Where Do We Use Blank Printed Circuit Boards?
So now you know what a blank PCB is, the types, and the materials. But what do we actually do with them? Spoiler alert: they’re everywhere! Let’s look at the most common blank PCB applications.
1. Electronic Prototyping
Before a company makes thousands of fancy circuit boards, engineers need to test their ideas. They use blank PCBs to build prototypes and make sure the design works. It’s like drawing a blueprint before building a house—better to make mistakes on a prototype than on the real thing!
Why it matters:
Saves time and money
Helps engineers fix problems early
2. Education and DIY Projects
Ever seen a science fair project with blinking LEDs? Chances are, it started with a blank PCB board. Students and hobbyists love blank PCBs because they make learning electronics easy and fun.
Common uses:
School projects
DIY gadgets
Maker communities
3. Small-Batch Custom Electronics
Not every company needs 10,000 circuit boards. Sometimes, they just need a small batch for testing or custom products. Blank PCBs make that possible because they can be easily modified and customized.
Examples:
Medical devices for research
Custom IoT devices
Specialized industrial tools
4. LED Lighting and Power Equipment
LEDs look cool, but they get hot—really hot. That’s why metal-core blank PCBs are used for LED lights and power equipment. They help spread the heat so the lights don’t burn out.
Where you see them:
LED lamps
Street lights
Power converters
5. Automotive and Medical Devices
Cars today are like rolling computers, and medical machines are super high-tech. Both need reliable PCBs that can handle heat, vibrations, and sometimes even flexibility. Blank PCBs make that possible.
Examples:
Car dashboards
Engine control units
Medical monitors and scanners

How to Choose the Right Blank Printed Circuit Board
Choosing the best blank PCB board for your project is like picking the right shoes—you don’t wear flip-flops to climb a mountain, right? Same idea here. Let’s break it down so you know exactly what to look for.
1. Think About Circuit Complexity
If your circuit is super simple, like turning on a light or powering a toy, a single-sided blank PCB works just fine. But if your design looks like a spaghetti monster with lots of connections, you’ll need a multilayer blank PCB to keep things neat.
Quick rule:
Simple = Single-sided
Medium complexity = Double-sided
Very complex (like a smartphone) = Multilayer
2. Check the Heat Factor
Does your project run hot? Like LEDs, power devices, or anything that gets warm after a few minutes? If yes, you need a board that can handle the heat. That’s where a metal-core blank PCB (usually aluminum) is your best friend. It keeps things cool and safe.
3. Price vs. Performance
Just like you wouldn’t buy a sports car to drive two blocks, don’t overspend on fancy boards for simple projects. FR4 blank PCBs are the most common because they’re strong and affordable. If you’re on a budget and your project is basic, go for FR4 or CEM material.
4. Do You Need Special Features?
Some projects need flexible PCBs that bend and twist. Others need high-frequency boards for fast signals (like in communication devices). If your design calls for something special, make sure you choose the right material and type.
Conclusion
So, what did we learn? Blank printed circuit boards come in many types—single-sided, double-sided, multilayer, flexible, even metal core. They’re made from different materials like FR4, aluminum, or polyimide, and they show up everywhere: in DIY projects, LED lights, cars, and even medical devices.
Now the big question: Which one is right for you?
Simple projects → Single-sided FR4
High power → Metal core
Tight spaces → Flexible PCB
Complex gadgets → Multilayer PCB
If you’re ready to buy blank printed circuit boards or need a custom blank PCB board, don’t overthink it. We can help you choose the best option for your project and even provide a fast quote.
Contact PCB MASTER today and let’s turn that blank board into something amazing!
FAQs
1. Can I cut a blank PCB at home?
Technically, yes! But be careful. Cutting a blank PCB is like cutting a sandwich with a hacksaw—you can do it, but it’s messy. If you really want to resize your board, use a PCB cutter or a small saw made for electronics. And always wear safety glasses! Cutting releases dust that you don’t want in your eyes or lungs. If it feels too tricky, let the PCB manufacturer make the right size for you—it’s safer and looks way better.
2. Can I reuse a blank PCB after soldering parts on it?
Not really. Once you solder components, the board isn’t “blank” anymore. You could try removing everything, but that’s like peeling cheese off pizza—you’ll never get it back to perfect. Plus, heating the board too many times can damage it. If you need a new design, it’s better to start with a fresh blank PCB. They’re not that expensive, and your project will work much better.
3. Do blank PCBs expire or go bad?
Blank PCBs don’t exactly “expire,” but they can get worse over time. Copper can oxidize (turn a bit dull or green), and moisture in the air can mess with the material. If you store them in a dry, clean place, they’ll last for years. But if your PCB looks like it’s been through a swamp or a barbecue, it’s time to get a new one.
